The outcomes of SGLT-2 inhibitor utilization in diabetic kidney transplant recipients
- PMID: 39567483
- PMCID: PMC11579355
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54171-8
The outcomes of SGLT-2 inhibitor utilization in diabetic kidney transplant recipients
Abstract
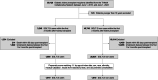
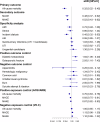
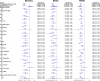
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) have demonstrated efficacy in reducing cardiovascular events and potentially improving kidney function in diabetic patients. This investigation analyzes the TriNetX database to assess the efficacy of SGLT-2i in diabetic kidney transplant recipients (KTR) concerning all-cause mortality, major adverse cardiac events (MACE), and major adverse kidney events (MAKE). The study includes type 2 diabetic patients over 18 who underwent kidney transplants between June 1, 2015, and June 1, 2023, with a focus on SGLT-2i use within the first three months post-transplant. After propensity score matching, the study compares 1970 SGLT-2i users with matched non-users. With a median follow-up of 3.4 years, SGLT-2i users showed significantly lower rates of all-cause mortality (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR]: 0.32), MACE (aHR: 0.48), and MAKE (aHR: 0.52). These findings indicate that SGLT-2i significantly reduces mortality and adverse events in diabetic KTR, underscoring its potential to improve post-transplant outcomes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Jenssen, T. & Hartmann, A. Post-transplant diabetes mellitus in patients with solid organ transplants. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.15, 172–188 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Kuo, H. T., Sampaio, M. S., Vincenti, F. & Bunnapradist, S. Associations of pretransplant diabetes mellitus, new-onset diabetes after transplant, and acute rejection with transplant outcomes: an analysis of the Organ Procurement and Transplant Network/United Network for Organ Sharing (OPTN/UNOS) database. Am. J. Kidney Dis.: J. Natl Kidney Found.56, 1127–1139 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Neal, B. et al. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med.377, 644–657 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

