Increased translation driven by non-canonical EZH2 creates a synthetic vulnerability in enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer
- PMID: 39567499
- PMCID: PMC11579030
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53874-2
Increased translation driven by non-canonical EZH2 creates a synthetic vulnerability in enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
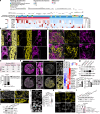
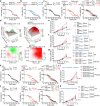
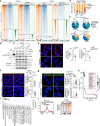
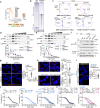
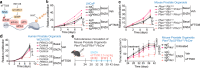
Overcoming resistance to therapy is a major challenge in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Lineage plasticity towards a neuroendocrine phenotype enables CRPC to adapt and survive targeted therapies. However, the molecular mechanisms of epigenetic reprogramming during this process are still poorly understood. Here we show that the protein kinase PKCλ/ι-mediated phosphorylation of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) regulates its proteasomal degradation and maintains EZH2 as part of the canonical polycomb repressive complex (PRC2). Loss of PKCλ/ι promotes a switch during enzalutamide treatment to a non-canonical EZH2 cistrome that triggers the transcriptional activation of the translational machinery to induce a transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) resistance program. The increased reliance on protein synthesis creates a synthetic vulnerability in PKCλ/ι-deficient CRPC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Davies, A. H., Beltran, H. & Zoubeidi, A. Cellular plasticity and the neuroendocrine phenotype in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol.15, 271–286 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R50 CA265332/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA274159/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM135362/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA274963/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K22 CA269707/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA246765/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R50 CA283476/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA277857/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA234162/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA277857/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- P50 CA211024/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R50CA283476/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R50CA265332/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R37 CA230617/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA250025/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA230913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA275846/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA265892/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA246765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA276308/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

