Bio-computational modeling, POM analysis and molecular dynamic simulation for novel synthetic quinolone and benzo[d][1,3]oxazine candidates as antimicrobial inhibitors
- PMID: 39567581
- PMCID: PMC11579483
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73972-x
Bio-computational modeling, POM analysis and molecular dynamic simulation for novel synthetic quinolone and benzo[d][1,3]oxazine candidates as antimicrobial inhibitors
Abstract
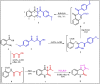
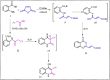
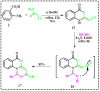
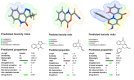
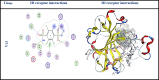
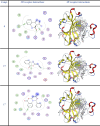
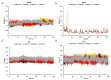
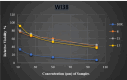
The current study offers a metal-free, direct, and successful synthesis technique for a new series of quinolinone and benzo[d][1,3]oxazine, along with an assessment of their biological activities. Heteroannulation of anthranilic acid with carbonyl-containing chemicals (aroyl pyruvate, ethyl acetoacetatete, maleic anhydride, and ethyl cyanoacetate) resulted in the desired quinolones and benzo[d][1,3]oxazines. This technique introduces a number of fundamental breakthroughs in organic synthesis, including metal-free catalysts, smart reaction conditions with column purification, and a wide functional scope. Furthermore, the structure of the newly synthesized chemical series was investigated and validated using spectroscopic techniques. The synthesized series were evaluated for antibacterial (against gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial strains) and antifungal activity. The quinolone and benzo[d][1,3]oxazine candidates had remarkable antibacterial action. Furthermore, molecular docking investigations corroborated the biological studies using the Molecular Operating Environment and Petro Osiris Molinspiration (POM) experiments, which confirmed the activity of compounds 8, 15, and 17. Our studies on the cytotoxic activity of various chemicals have demonstrated that these compounds exhibit minimal toxicity. Specifically, when comparing the cytotoxic effects on human lung fibroblast (WI38) cells to those of Doxorubicin, a well-known chemotherapy agent, compounds 8, 15, and 17 showed weak cytotoxic effects on the normal WI38 cells. This indicates that these compounds may possess some level of selectivity and reduced toxicity towards normal cells, suggesting potential for further exploration as antibacterial agents with a safer profile for normal cells.
Keywords: Antimicrobial; Bio-computational modeling; Molecular dynamic simulation; POM analysis; Quinolone.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Vigliotta, G. et al. New Compounds for a good old Class: Synthesis of Two Β-lactam Bearing Cephalosporins and Their Evaluation with a Multidisciplinary Approach28p. 115302 (Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2020). 4. - PubMed
-
- Mostafa, S. M. et al. New quinoline-2-one/thiazolium bromide derivatives; synthesis, characterization and mechanism of formation. J. Mol. Struct.1239, 130501 (2021). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

