Intrinsic GATA4 expression sensitizes the aortic root to dilation in a Loeys-Dietz syndrome mouse model
- PMID: 39567770
- PMCID: PMC11634776
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-024-00562-5
Intrinsic GATA4 expression sensitizes the aortic root to dilation in a Loeys-Dietz syndrome mouse model
Abstract
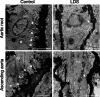
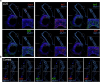
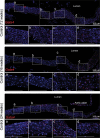
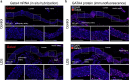
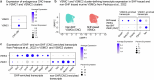
Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) is a connective tissue disorder caused by mutations that decrease transforming growth factor-β signaling. LDS-causing mutations increase the risk of aneurysm throughout the arterial tree, yet the aortic root is a site of heightened susceptibility. Here we investigate the heterogeneity of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) in the aorta of Tgfbr1M318R/+ LDS mice by single-cell transcriptomics to identify molecular determinants of this vulnerability. Reduced expression of components of the extracellular matrix-receptor apparatus and upregulation of stress and inflammatory pathways were observed in all LDS VSMCs. However, regardless of genotype, a subset of Gata4-expressing VSMCs predominantly located in the aortic root intrinsically displayed a less differentiated, proinflammatory profile. A similar population was also identified among aortic VSMCs in a human single-cell RNA sequencing dataset. Postnatal VSMC-specific Gata4 deletion reduced aortic root dilation in LDS mice, suggesting that this factor sensitizes the aortic root to the effects of impaired transforming growth factor-β signaling.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Update of
-
Intrinsic Gata4 expression sensitizes the aortic root to dilation in a Loeys-Dietz syndrome mouse model.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 5:rs.3.rs-4420617. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4420617/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024 Dec;3(12):1468-1481. doi: 10.1038/s44161-024-00562-5. PMID: 38883722 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Chou, E., Pirruccello, J. P., Ellinor, P. T. & Lindsay, M. E. Genetics and mechanisms of thoracic aortic disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol.20, 168–180 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Loeys, B. L. et al. A syndrome of altered cardiovascular, craniofacial, neurocognitive and skeletal development caused by mutations in TGFBR1 or TGFBR2. Nat. Genet.37, 275–281 (2005). - PubMed
-
- van de Laar, I. M. et al. Mutations in SMAD3 cause a syndromic form of aortic aneurysms and dissections with early-onset osteoarthritis. Nat. Genet.43, 121–126 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 HL163924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31HL163924/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01 HL147947/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL147947/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- S10 OD023548/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
