Viral N protein hijacks deaminase-containing RNA granules to enhance SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis
- PMID: 39567830
- PMCID: PMC11649915
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00314-y
Viral N protein hijacks deaminase-containing RNA granules to enhance SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis
Abstract
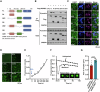
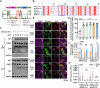
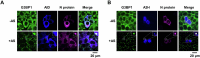
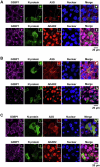
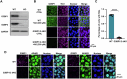
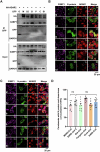
Host cell-encoded deaminases act as antiviral restriction factors to impair viral replication and production through introducing mutations in the viral genome. We sought to understand whether deaminases are involved in SARS-CoV-2 mutation and replication, and how the viral factors interact with deaminases to trigger these processes. Here, we show that APOBEC and ADAR deaminases act as the driving forces for SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis, thereby blocking viral infection and production. Mechanistically, SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein, which is responsible for packaging viral genomic RNA, interacts with host deaminases and co-localizes with them at stress granules to facilitate viral RNA mutagenesis. N proteins from several coronaviruses interact with host deaminases at RNA granules in a manner dependent on its F17 residue, suggesting a conserved role in modulation of viral mutagenesis in other coronaviruses. Furthermore, mutant N protein bearing a F17A substitution cannot localize to deaminase-containing RNA granules and leads to reduced mutagenesis of viral RNA, providing support for its function in enhancing deaminase-dependent viral RNA editing. Our study thus provides further insight into virus-host cell interactions mediating SARS-CoV-2 evolution.
Keywords: Deaminases; Innate Immunity; Mutagenesis; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of A-to-I RNA editing in infections by RNA viruses: Possible implications for SARS-CoV-2 infection.Clin Immunol. 2021 May;226:108699. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2021.108699. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33639276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 N protein coordinates viral particle assembly through multiple domains.J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0103624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01036-24. Epub 2024 Oct 16. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39412257 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for host-dependent RNA editing in the transcriptome of SARS-CoV-2.Sci Adv. 2020 Jun 17;6(25):eabb5813. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb5813. eCollection 2020 Jun. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32596474 Free PMC article.
-
Host-directed editing of the SARS-CoV-2 genome.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 29;538:35-39. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.092. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33234239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 haplotypes and genomic sequences during 2020 in Victoria, Australia, in the context of putative deficits in innate immune deaminase anti-viral responses.Scand J Immunol. 2021 Nov;94(5):e13100. doi: 10.1111/sji.13100. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Scand J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34940992 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Perillaldehyde Improves Parkinson-Like Deficits by Targeting G3BP Mediated Stress Granule Assembly in Preclinical Models.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(14):e2412152. doi: 10.1002/advs.202412152. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39951026 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3 regulates PRRSV replication by suppressing interferon beta through autophagy-mediated IKKε degradation.J Virol. 2025 Jul 22;99(7):e0009825. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00098-25. Epub 2025 Jun 23. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40548751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aizawa H, Sawada J, Hideyama T, Yamashita T, Katayama T, Hasebe N, Kimura T, Yahara O, Kwak S (2010) TDP-43 pathology in sporadic ALS occurs in motor neurons lacking the RNA editing enzyme ADAR2. Acta Neuropathol 120:75–84 - PubMed
-
- Alberti S (2017) Phase separation in biology. Curr Biol 27:R1097–R1102 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82302497/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 82188102/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 22177073/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 32070153/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 2021YFA0804702/MOST | National Key Research and Development Program of China (NKPs)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

