Melanin-like nanoparticles as a potential novel therapeutic approach in ADPKD
- PMID: 39567833
- PMCID: PMC11730632
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-024-00173-4
Melanin-like nanoparticles as a potential novel therapeutic approach in ADPKD
Abstract
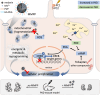
In this issue of EMBO Molecular Medicine, Sun and colleagues report the development of a novel therapeutic approach, and preclinical proof-of-concept evidence of its efficacy, for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) (Sun et al, 2024).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cassina L, Chiaravalli M, Boletta A (2020) Increased mitochondrial fragmentation in polycystic kidney disease acts as a modifier of disease progression. FASEB J 34:6493–6507 - PubMed
-
- Kahveci AS, Barnatan TT, Kahveci A, Adrian AE, Arroyo J, Eirin A, Harris PC, Lerman A, Lerman LO, Torres VE et al (2020) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial abnormalities contribute to decreased endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression and renal disease progression in early experimental polycystic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci 21:1994 - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

