Radiology-pathology correlation: Rosai-Dorfman disease
- PMID: 39567877
- PMCID: PMC11580121
- DOI: 10.1177/19714009241303077
Radiology-pathology correlation: Rosai-Dorfman disease
Abstract
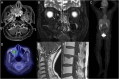
Rosai-Dorfman Disease (RDD), also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, is a rare non-Langerhans cell histiocytic neoplasm. Although the disease classically presents as massive painless lymphadenopathy in young adults, RDD can also involve the central nervous system in some patients. CNS lesions, can cause headaches, neurologic deficits, and even neurologic deficits. The imaging appearance of CNS RDD typically mimics that of meningiomas: well-circumscribed dural-based lesions that often have dural tails. However, some imaging clues also exist that might help a radiologist recognize RDD, even before histopathologic confirmation. This radiology-pathology report of a patient with CNS RDD highlights the most pertinent clinical, imaging, and pathologic features of CNS RDD, and discusses what the neuroradiologist needs to know about the disease.
Keywords: MRI; Tumor; pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

