Chloroplast genome of four Amorphophallus species: genomic features,comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships among Amorphophallus species
- PMID: 39567899
- PMCID: PMC11580329
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-11053-z
Chloroplast genome of four Amorphophallus species: genomic features,comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships among Amorphophallus species
Abstract
Background: The genus Amorphophallus (Araceae) contains approximately 250 species, most of which have high ecological and economic significance. The chloroplast genome data and the comprehensive analysis of the chloroplast genome structure of Amorphophallus is limited. In this study, four chloroplast genomes of Amorphophallus were sequenced and assembled. For the first time, comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes were conducted on the 13 Amorphophallus species in conjunction with nine published sequences.
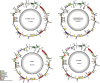
Results: The Amorphophallus chloroplast genomes exhibited typical quadripartite structures with lengths ranging from 164,417 to 177,076 bp. These structures consisted of a large single copy (LSC, 90,705 - 98,561 bp), a small single copy (SSC, 14,172 - 21,575 bp), and a pair of inverted repeats (IRs, 26,225 - 35,204 bp). The genomes contain 108 - 113 unique genes, including 76 - 79 protein-coding genes, 28 - 29 tRNA genes, and 4 rRNA genes. The molecular structure, gene order, content, codon usage, long repeats, and simple sequence repeats (SSRs) within Amorphophallus were generally conserved. However, several variations in intron loss and gene expansion on the IR-SSC boundary regions were found among these 13 genomes. Four mutational hotspot regions, including trnM-atpE, atpB, atpB-rbcL and ycf1 were identified. They could identify and phylogeny future species in the genus Amorphophallus. Positive selection was found for rpl36, ccsA, rpl16, rps4, rps8, rps11, rps12, rps14, clpP, rps3, ycf1, rpl20, rps2, rps18, rps19, atpA, atpF, rpl14, rpoA, rpoC1, rpoC2 and rps15 based on the analyses of Ka/Ks ratios. Phylogenetic inferences based on the complete chloroplast genomes revealed a sister relationship between Amorphophallus and Caladieae. All Amorphophallus species formed a monophyletic evolutionary clade and were divided into three groups, including CA-II, SEA, and CA-I. Amorphophallus albus, A. krausei, A. kachinensis and A. konjac were clustered into the CA-II clade, A. paeoniifolius and A. titanum were clustered into the SEA clade, A. muelleri 'zhuyajin1', Amorphophallus sp, A. coaetaneus, A. tonkinensis and A. yunnanensis were clustered into CA- I clade.
Conclusions: The genome structure and gene content of Amorphophallus chloroplast genomes are consistent across various species. In this study, the structural variation and comparative genome of chloroplast genomes of Amorphophallus were comprehensively analyzed for the first time. The results provide important genetic information for species classification, identification, molecular breeding, and evolutionary exploration of the genus Amorphophallus.
Keywords: Amorphophallus; Chloroplast genome; Genome comparison; Phylogenetic analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The materials involved in the article does not an endangered or protected species; therefore, permission is not required to collect this species. Research on these species, including the collection of plant materials has been carried out in accordance with guidelines provided by Kunming University. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Claudel C, Buerki S, Chatro LW, Antonelli A, Alvarez N, Hetterscheid WLA. Large-scale phylogenetic analysis of Amorphophallus (Araceae) derived from nuclear and plastid sequences reveals new subgeneric delineation. J Linn Soc Bot. 2017;184:32–45.
-
- Islam F, Labib RK, Zehravi M, Lami MS, Das R, Singh LP, Mandhadi JR, Balan P, Khan J, Khan SL, Nainu F, Nafady MH, Rab SO, Emran TB, Wilairatana P. Genus Amorphophallus: a comprehensive overview on phytochemistry, ethnomedicinal uses, and pharmacological activities. Plants (Basel). 2023;12(23):3945. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao C, She X, Liu E, et al. A mixed ploidy natural population of Amorphophallus muelleri provides an opportunity to trace the evolution of Amorphophallus karyotype. J Genet. 2021;100:10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 202401AU070020;202201AU070043; 202101BA070001-174; 202201AT070113; 202101AO070075/Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- 202401AU070020;202201AU070043; 202101BA070001-174; 202201AT070113; 202101AO070075/Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- 2024J0771/Yunnan Provincial Department of Education Science Research Fund Project
- 2024J0771/Yunnan Provincial Department of Education Science Research Fund Project
- YJL23026, YJL23010, YJL23005, YJL23007/Kunming University Talent Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

