Functional redundancy buffers the effect of poly-extreme environmental conditions on southern African dryland soil microbial communities
- PMID: 39568064
- PMCID: PMC11636270
- DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiae157
Functional redundancy buffers the effect of poly-extreme environmental conditions on southern African dryland soil microbial communities
Abstract
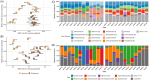
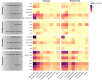
Drylands' poly-extreme conditions limit edaphic microbial diversity and functionality. Furthermore, climate change exacerbates soil desiccation and salinity in most drylands. To better understand the potential effects of these changes on dryland microbial communities, we evaluated their taxonomic and functional diversities in two Southern African dryland soils with contrasting aridity and salinity. Fungal community structure was significantly influenced by aridity and salinity, while Bacteria and Archaea only by salinity. Deterministic homogeneous selection was significantly more important for bacterial and archaeal communities' assembly in hyperarid and saline soils when compared to those from arid soils. This suggests that niche partitioning drives bacterial and archaeal communities' assembly under the most extreme conditions. Conversely, stochastic dispersal limitations drove the assembly of fungal communities. Hyperarid and saline soil communities exhibited similar potential functional capacities, demonstrating a disconnect between microbial structure and function. Structure variations could be functionally compensated by different taxa with similar functions, as implied by the high levels of functional redundancy. Consequently, while environmental selective pressures shape the dryland microbial community assembly and structures, they do not influence their potential functionality. This suggests that they are functionally stable and that they could be functional even under harsher conditions, such as those expected with climate change.
Keywords: dryland soils; edaphic microbial communities; functional redundancy; metabarcoding; niche partitioning; shotgun metagenomics.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson IC, Cairney JWG. Diversity and ecology of soil fungal communities: increased understanding through the application of molecular techniques. Environ Microbiol. 2004;6:769–79. - PubMed
-
- Andrews S. FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. 2010. https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (27 March 2021, date last accessed).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

