A scoping review of dementia education programs to assess for the inclusion of culture
- PMID: 39568104
- PMCID: PMC12276392
- DOI: 10.1177/14713012241300592
A scoping review of dementia education programs to assess for the inclusion of culture
Abstract
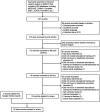
This scoping review examined literature on dementia education programs (DEPs) for healthcare providers and students. The search was conducted using the Discover! search engine that includes 63 databases. The review included a total of 25 articles that met the eligibility criteria. There were numerous DEPs that varied by frequency and duration, mode of delivery, content, target population, program evaluation measures, and outcomes. Most involved nursing staff and students and took place in Canada, the US, and the UK. The most common delivery mode was a one-time in-person session and a wide variety of topics were covered, both general (e.g., understanding dementia) and specific (e.g., driving, delirium). Twenty different tools were used to measure primarily changes in knowledge and attitudes, with little attention paid to performance and care provision. Only three studies on DEPs focused on culture in terms of race and ethnicity. The implications of this scoping review for education are that DEPs need to meaningfully address culture and culturally safe care in order to respond to the increasing diversity of older adults and care providers. In terms of future research on DEPs, program evaluation must attend to the importance of consistent measures, translation of knowledge to practice, and sustainability.
Keywords: culture; dementia; education; health care; nursing; program evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Similar articles
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
Palliative care interventions in advanced dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Dec 2;12(12):CD011513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011513.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 28;9:CD011513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011513.pub3. PMID: 27911489 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Cultural competence education for health professionals.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 5;2014(5):CD009405. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009405.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24793445 Free PMC article.
-
Faculty development initiatives designed to promote leadership in medical education. A BEME systematic review: BEME Guide No. 19.Med Teach. 2012;34(6):483-503. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2012.680937. Med Teach. 2012. PMID: 22578043
-
The effectiveness of tools used to evaluate successful critical decision making skills for applicants to healthcare graduate educational programs: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 May 15;13(4):231-75. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2322. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447081
References
-
- References marked with an * indicate studies included in this scoping review.
-
- Advanced Gerontological Education Inc . (nd). GPA as a critical component in a culture of person-centred care. https://ageinc.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/2022/01/GPAAsCriticalComponentOf...
-
- AGE Inc . (2021). Gentle persuasive approaches basics workbook (4th ed.). AGE Inc.
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease International [ADI] . (2022). From plan to impact V: WHO global action plan: The time to act is now. ADI. https://www.alzint.org/what-we-do/adi-conference/previous-international-...
-
- Arksey H., O’Malley L. (2005). Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 8(1), 19–32. DOI: 10.1080/1364557032000119616. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous