Hierarchically Structured and Tunable Hydrogel Patches: Design, Characterization, and Application
- PMID: 39568251
- PMCID: PMC11753498
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.202407311
Hierarchically Structured and Tunable Hydrogel Patches: Design, Characterization, and Application
Abstract
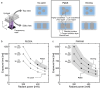
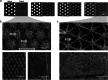
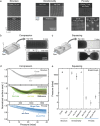
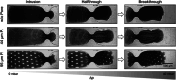
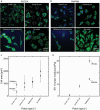
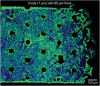
Recent studies show the importance of hydrogel geometry for various applications, such as encoding, micromachines, or tissue engineering. However, fabricating hydrogel structures with micrometer-sized features, advanced geometry, and precise control of porosity remains challenging. This work presents hierarchically structured hydrogels, so-called hydrogel patches, with internally deviating regions on a micron-scale. These regions are defined in a one-step, high-throughput fabrication process via stop-flow lithography. Between the specified projection pattern during fabrication, an interconnecting lower crosslinked and more porous hydrogel network forms, resulting in at least two degrees of crosslinking within the patches. A detailed investigation of patch formation is performed for two material systems and pattern variations, revealing basic principles for reliable patch formation. In addition to the two defined crosslinked regions, further regions are implemented in the patches by adapting the pattern accordingly. The variations in pattern geometry impact the mechanical characteristics of the hydrogel patches, which display pattern-dependent compression behavior due to predefined compression points. Cell culture on patches, as one possible application, reveals that the patch pattern determines the cell area of L929 mouse fibroblasts. These results introduce hierarchically structured hydrogel patches as a promising and versatile platform system with high customizability.
Keywords: biomaterial; hierarchical cellular material; hydrogel; porosity; projection lithography.
© 2024 The Author(s). Small published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
3D printed multi-growth factor delivery patches fabricated using dual-crosslinked decellularized extracellular matrix-based hybrid inks to promote cerebral angiogenesis.Acta Biomater. 2023 Feb;157:137-148. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.11.050. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36460287
-
Transfer stamping of human mesenchymal stem cell patches using thermally expandable hydrogels with tunable cell-adhesive properties.Biomaterials. 2015 Jun;54:44-54. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.03.016. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 25907038
-
Hierarchically Structured Porous Poly(2-oxazoline) Hydrogels.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016 Jan;37(1):93-99. doi: 10.1002/marc.201500495. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016. PMID: 26474191
-
Hydrogel-based cardiac patches for myocardial infarction therapy: Recent advances and challenges.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Nov 7;29:101331. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101331. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39619639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in gelatin-based hydrogel systems for biomedical applications: A state-of-the-art review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Dec 31;253(Pt 5):127143. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127143. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37793512 Review.
References
-
- Agrawal G., Agrawal R., Small 2018, 14, 1801724. - PubMed
-
- Aizenberg J., Levkin P. A., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 26.
-
- Choi E., Chang H.‐K., Jun I., Park K. M., Shin H., Park K. D., Park J., in IEEE Int. Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, IEEE, New York: 2011, pp. 1890–1894.
-
- Gerardo‐Nava J. L., Jansen J., Günther D., Klasen L., Thiebes A. L., Niessing B., Bergerbit C., Meyer A. A., Linkhorst J., Barth M., Akhyari P., Stingl J., Nagel S., Stiehl T., Lampert A., Leube R., Wessling M., Santoro F., Ingebrandt S., Jockenhoevel S., Herrmann A., Fischer H., Wagner W., Schmitt R. H., Kiessling F., Kramann R., de Laporte L., Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2023, 12, 2301030. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu Y., Chen Z., Xu J., GreenChE 2024, 5, 16.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

