Identifying the quality markers and optimizing the processing of Gastrodiae rhizoma to treat brain diseases
- PMID: 39568583
- PMCID: PMC11576197
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1396825
Identifying the quality markers and optimizing the processing of Gastrodiae rhizoma to treat brain diseases
Abstract
Background: Gastrodiae rhizoma (GR) refers to the dried tuber of Gastrodia elata Bl. and has been used for many centuries to treat brain diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, major depressive disorder, and cerebral ischemia. However, the processing of GR is complex and varied, resulting in unstable clinical treatment effects. The processing protocols significantly affect the active ingredients and curative effects of GR. We can optimize the processing of GR by identifying quality markers to treat brain diseases.
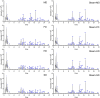
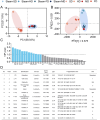
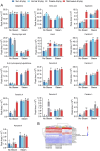
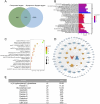
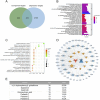
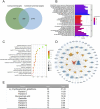
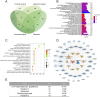
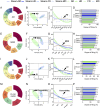
Methods: Fresh tubers of G. elata Bl. were processed under eight different protocols, and their resulting contents of potentially bioactive compounds were compared using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry to screen the potential quality markers of GR through stoichiometric analysis. The potential quality markers of GR targeting Alzheimer's disease, major depressive disorder, and cerebral ischemia were identified by network pharmacology, and the potentially neuroprotective effects of these components were validated through simulated docking to likely protein targets. Finally, a fit degree analysis was carried out using different composition ratios and proportions of the disease component degree value, and the therapeutic effects of different processing methods on Alzheimer's disease, major depressive disorder, and cerebral ischemia were outlined clearly.
Results: We identified 32 potential therapeutic components and screened 13 quality markers in GR, of which five quality markers (galactinol, glucosyringic acid, parishins C and E, and S-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-glutathione) showed efficacy against all three brain diseases. Furthermore, steaming and microwave-drying during processing can optimize the components of these quality markers for treating the three diseases.
Conclusion: Processing protocols significantly affect the therapeutic components of GR and may also impact its effectiveness in treating brain diseases. Accordingly, optimizing the processing methods of GR to correspond to different therapeutic purposes may improve its efficacy against brain diseases.
Keywords: Gastrodia elata BL; fresh-cut processing; metabolomics; network pharmacology; neuroprotection; quality markers.
Copyright © 2024 Fu, Xu, Zhang, Kang, Yang, Guo, Zhang, Zhou and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer HP declared a shared affiliation with the author CK to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures

References
-
- Gonzalez-Juarez D. E., Escobedo-Moratilla A., Flores J., Hidalgo-Figueroa S., Martinez-Taguena N., Morales-Jimenez J., et al. (2020). A review of the ephedra genus: distribution, ecology, ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties. Molecules 25 (14), 3283. 10.3390/molecules25143283 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hsieh C. L., Chen C. L., Tang N. Y., Chuang C. M., Hsieh C. T., Chiang S. Y., et al. (2005). Gastrodia elata BL mediates the suppression of nNOS and microglia activation to protect against neuronal damage in kainic acid-treated rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 33 (4), 599–611. 10.1142/S0192415X0500320X - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

