Tinosporae Radix attenuates acute pharyngitis by regulating glycerophospholipid metabolism and inflammatory responses through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
- PMID: 39568590
- PMCID: PMC11576305
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1491321
Tinosporae Radix attenuates acute pharyngitis by regulating glycerophospholipid metabolism and inflammatory responses through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
Abstract
Introduction: With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the incidence and prevalence of acute pharyngitis (AP) have increased significantly. Tinosporae Radix (TR) is a vital medication utilized in the treatment of pharyngeal and laryngeal ailments, especially AP. The study endeavors to explore unclear molecular mechanisms of TR in addressing AP.
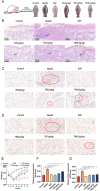
Methods: Network pharmacology and metabolomics analyses of effect of TR on AP were conducted, and apossible pathway was validated both in vivo using the acute pharyngitis rat model and in vitro using the LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells model, through techniques such as histopathological examinations, immunohistochemical technology, ELISA, RT-qPCR, and Western blotting to systematically explore the possible mechanisms underlying the inhibition of AP by TR.
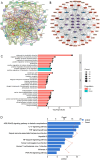
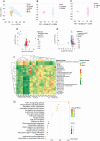
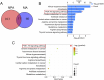
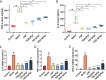
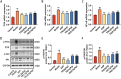
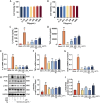
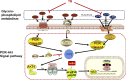
Results and discussion: Network pharmacology analysis identified several key targets, including PIK3CA, IL6, AKT1, TNF, and PTGS2, alongside pivotal signaling pathways such as IL-17, TNF, Hepatitis B, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), Influenza A, and the PI3K-Akt pathway. Most of them are closely associated with inflammation. Then, wide-target metabolomics analysis showed that TR downregulated substances within the glycerophospholipid metabolic pathway, and modulated the PI3K-Akt pathway. The integrated findings from network pharmacology and metabolomics underscored the pivotal role of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and the attenuation of inflammatory responses. Finally, in vitro and in vivo experiments have shown that TR can inhibit inflammatory factors such as IL-6, TNF - α, and COX-2, downregulate targets such as PI3K and AKT on the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and thereby alleviate the inflammatory response of AP. Our study demonstrated that TR exerts an anti-AP effect through suppression of release of inflammatory factors and modulation of glycerophospholipid metabolism via suppressing the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.
Keywords: PI3K-Akt signaling pathway; Tinosporae Radix; acute pharyngitis; glycerophospholipid metabolism; inflammatory responses.
Copyright © 2024 Lu, Huang, Zhou, Jiang, Chen, Du, Zhou, Wen, Pei and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of Yinhuang Hanhua dropping pill on acute pharyngitis via a systematic "Compound-Target-Pathway" analysis.Phytomedicine. 2025 Apr;139:156423. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156423. Epub 2025 Jan 26. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39951971
-
Integrative network pharmacology and multi-omics to study the potential mechanism of Niuhuang Shangqing Pill on acute pharyngitis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Feb 10;338(Pt 3):119100. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119100. Epub 2024 Nov 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39547363
-
Dihydrosanguinarine based RNA-seq approach couple with network pharmacology attenuates LPS-induced inflammation through TNF/IL-17/PI3K/AKT pathways in mice liver.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Aug;109:108779. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108779. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35490666
-
The mechanism of action of paeoniae radix rubra-angelicae sinensis radix drug pair in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis through PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 13;14:1113810. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1113810. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36992829 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect of Hosta plantaginea (Lam.) Aschers flowers on acute pharyngitis through inhibition of multi-inflammatory pathways in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt A):116966. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116966. Epub 2023 Jul 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37499845
References
-
- Bamford A., Masini T., Williams P., Sharland M., Gigante V., Dixit D., et al. (2024). Tackling the threat of antimicrobial resistance in neonates and children: outcomes from the first WHO-convened Paediatric Drug Optimisation exercise for antibiotics. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health, Bisno A L (2001). Acute Pharyngitis. New Engl. J. Med. 344 (3), 205–211. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

