Application of CT-based foundational artificial intelligence and radiomics models for prediction of survival for lung cancer patients treated on the NRG/RTOG 0617 clinical trial
- PMID: 39568594
- PMCID: PMC11576354
- DOI: 10.1093/bjro/tzae038
Application of CT-based foundational artificial intelligence and radiomics models for prediction of survival for lung cancer patients treated on the NRG/RTOG 0617 clinical trial
Abstract
Objectives: To apply CT-based foundational artificial intelligence (AI) and radiomics models for predicting overall survival (OS) for patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
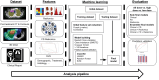
Methods: Data for 449 patients retrospectively treated on the NRG Oncology/Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 0617 clinical trial were analyzed. Foundational AI, radiomics, and clinical features were evaluated using univariate cox regression and correlational analyses to determine independent predictors of survival. Several models were fit using these predictors and model performance was evaluated using nested cross-validation and unseen independent test datasets via area under receiver-operator-characteristic curves, AUCs.
Results: For all patients, the combined foundational AI and clinical models achieved AUCs of 0.67 for the Random Forest (RF) model. The combined radiomics and clinical models achieved RF AUCs of 0.66. In the low-dose arm, foundational AI alone achieved AUC of 0.67, while AUC for the ensemble radiomics and clinical models was 0.65 for the support vector machine (SVM). In the high-dose arm, AUC values were 0.67 for combined radiomics and clinical models and 0.66 for the foundational AI model.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated encouraging results for application of foundational AI and radiomics models for prediction of outcomes. More research is warranted to understand the value of ensemble models toward improving performance via complementary information.
Advances in knowledge: Using foundational AI and radiomics-based models we were able to identify significant signatures of outcomes for NSCLC patients retrospectively treated on a national cooperative group clinical trial. Associated models will be important for application toward prospective patients.
Keywords: cross-validation; feature selection; foundational model; machine learning; non-small cell lung cancer; prognosis; radiomics.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Institute of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by OncLive—Honoraria and Varian Medical Systems—grant funding to institution [to K.M.A.].
Figures

Similar articles
-
An [18F]FDG PET/3D-ultrashort echo time MRI-based radiomics model established by machine learning facilitates preoperative assessment of lymph node status in non-small cell lung cancer.Eur Radiol. 2024 Jan;34(1):318-329. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09978-2. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37530809
-
PET/CT Radiomic Features: A Potential Biomarker for EGFR Mutation Status and Survival Outcome Prediction in NSCLC Patients Treated With TKIs.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 21;12:894323. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.894323. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35800046 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics-Clinical AI Model with Probability Weighted Strategy for Prognosis Prediction in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 25;11(8):2093. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082093. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626590 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Artificial Intelligence Models in Predicting Lung Cancer Recurrence: A Gene Biomarker-Driven Review.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 5;17(11):1892. doi: 10.3390/cancers17111892. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review on the Application of Artificial Intelligence for Predicting Postsurgical Recurrence Risk in Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Computed Tomography, Positron Emission Tomography, and Clinical Data.J Med Radiat Sci. 2025 Sep;72(3):280-296. doi: 10.1002/jmrs.860. Epub 2025 Jan 23. J Med Radiat Sci. 2025. PMID: 39844750 Review.
Cited by
-
Baseline Radiomics as a Prognostic Tool for Clinical Benefit from Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in Inoperable NSCLC Without Activating Mutations.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 27;17(11):1790. doi: 10.3390/cancers17111790. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507271 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing artificial intelligence to address immune response heterogeneity in low-dose radiation therapy.World J Radiol. 2025 May 28;17(5):108011. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i5.108011. World J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40503475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vallières M, Freeman CR, Skamene SR, El Naqa I.. A radiomics model from joint FDG-PET and MRI texture features for the prediction of lung metastases in soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities. Phys Med Biol. 2015;60(14):5471-5496. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

