Laparoscopic Heller myotomy versus peroral endoscopic myotomy in children with esophageal achalasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39568706
- PMCID: PMC11574155
- DOI: 10.20524/aog.2024.0923
Laparoscopic Heller myotomy versus peroral endoscopic myotomy in children with esophageal achalasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Currently, laparoscopic Heller myotomy (LHM) and peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) are the best treatment modalities for esophageal achalasia in children. The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to compare the efficacy of LHM and POEM.
Methods: A systematic literature search was performed in PubMed/Medline, Google Scholar and Web of Science for original articles comparing LHM and POEM. All articles were analyzed with respect to operation duration, length of hospital stay, pre- and postoperative Eckardt score (ES), and pre- and postoperative lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure.
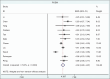
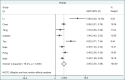
Results: A total of 32 articles, reporting on 800 children, were selected and reviewed. Because of missing diagnostic values of ES and LES in the LHM group, the meta-analysis was limited to the POEM results. According to the random-effects model, the mean ES difference between pre- and post-operation was 4.387 (95% confidence interval [CI] 3.799-4.974), significantly different to zero (z=14.64, P<0.001), while the mean LES pressure difference was 3.63 mmHg mmHg (95%CI 2247-3.879), significantly different to zero (z=7.36, P<0.001). Operation duration was 130.15 min (95%CI 62.59-197.71) for the LHM method and 83.64 min (95%CI 55.14-112.14) for POEM. The pooled estimate of length of hospital stay was 3.4 days (95%CI 2.6-4.44) and it was comparable between the 2 methods.
Conclusions: POEM has positive outcomes regarding ES and LES pressure pre- and postoperatively, as well as operation duration, while the length of hospitalization was comparable between POEM and LHM. Well-designed studies are warranted to further clarify differences between the 2 methods.
Keywords: Eckardt score; Lower esophageal sphincter pressure; length of hospitalization; operation time; outcome.
Copyright: © 2024 Hellenic Society of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None
Figures


References
-
- Shieh TY, Chen CC, Chou CK, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of peroral endoscopic myotomy for esophageal achalasia:a multicenter study in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. 2022;121:1123–1132. - PubMed
-
- van Lennep M, van Wijk MP, Omari TIM, Salvatore S, Benninga MA, Singendonk MMJ European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Motility Working Group. Clinical management of pediatric achalasia:a survey of current practice. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2019;68:521–526. - PubMed
-
- Choné A, Familiari P, von Rahden B, et al. Multicenter evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety of per-oral endoscopic myotomy in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2019;69:523–527. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
