Impact of Permissive Hypercapnia on Postoperative Early Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain in Elderly Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Surgery: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39568861
- PMCID: PMC11576572
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S492456
Impact of Permissive Hypercapnia on Postoperative Early Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain in Elderly Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Surgery: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: The effects of intraoperative permissive hypercapnia (PaCO2 of 45-55 mmHg) on the central nervous system remain unclear. Neurofilament light chain (NfL, a protein found in the axons and nerve fibers of neurons) has been associated with central nervous system disorders. This study investigated the effect of intraoperative permissive hypercapnia on plasma NfL concentration 1 day postoperatively, and in turn on the central nervous system, during laparoscopic surgery.
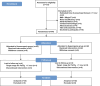
Methods: This investigation was a prospective, single-blind randomized controlled trial. Eighty-four individuals aged above 60 years were randomly allocated to either the normocapnia group with an PaCO2 of 35-45 mmHg (n=42) or the hypercapnia group with a PaCO2 of 45-55 mmHg (n=42). The primary outcome was the 1-day postoperative plasma NfL concentration. Secondary outcomes included the area under the curve (AUC) values for PaCO2 and regional cerebral oxygen saturation (rSO2). The Mann-Whitney U-test was mainly used to analyze the outcomes.
Results: The final analysis included 38 and 40 patients in the normocapnia and hypercapnia groups, respectively. There was no statistically significant difference observed between the groups regarding the preoperative and 1-day postoperative plasma NfL concentration (14.0 [11.1, 19.9] vs 16.3 [9.06, 19.9] pg/mL, P>0.05; 23.4 [16.8, 32.3] vs 21.5 [15.6, 29.9] pg/mL, P>0.05, respectively). However, in both groups, the postoperative plasma concentration of NfL showed a significant increase when compared with the preoperative levels (both P < 0.001). The AUCs of PaCO2 and rSO2 from the beginning to the end of the pneumoperitoneum were significantly higher in the hypercapnia group compared with the normocapnia group (both P<0.05).
Conclusion: Our results indicate that intraoperative permissive hypercapnia targeting a PaCO2 of 45-55 mmHg does not significantly influence postoperative early plasma NfL elevation levels in elderly patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. During general anesthesia, intraoperative permissive hypercapnia might not significantly impact the central nervous system.
Keywords: general anesthesia; hypercapnia; laparoscopic surgery; neurofilament light chain.
© 2024 Xi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the Effects of Normocapnia and Mild Hypercapnia on the Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter and Regional Cerebral Oxygen Saturation in Patients Undergoing Gynecological Laparoscopy with Total Intravenous Anesthesia.J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 14;10(20):4707. doi: 10.3390/jcm10204707. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34682830 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of targeted mild hypercapnia versus normocapnia on cerebral oxygen saturation in patients undergoing laparoscopic hepatectomy under low central venous pressure: a prospective, randomized controlled study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Jul 31;23(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02220-y. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37525100 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of permissive hypercapnia on intraoperative cerebral oxygenation and early postoperative cognitive function in older patients with non-acute fragile brain function undergoing laparoscopic colorectal surgery: protocol study.BMC Geriatr. 2023 Sep 21;23(1):581. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04125-4. BMC Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 37735369 Free PMC article.
-
Progress on the Effects of Permissive Hypercapnia on the CNS During the Intraoperative Period: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 29;16(8):e68087. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68087. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39347154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Targeted Hypercapnia on Mortality and Length of Stay of Post-cardiac Arrest Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 May 19;16(5):e60617. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60617. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38894798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Permissive hypercapnia combined with goal-directed fluid therapy improve postoperative mental health in elderly patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery.World J Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 19;15(7):106023. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.106023. eCollection 2025 Jul 19. World J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40740450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joe YE, Lee CY, Kim N, et al. Effect of permissive hypercarbia on lung oxygenation during one-lung ventilation and postoperative pulmonary complications in patients undergoing thoracic surgery: a prospective randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2023;40(9):691–698. doi:10.1097/EJA.0000000000001873 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources