Chronic Inflammation and Age-Related Hearing: Based on Mendelian Randomization
- PMID: 39569023
- PMCID: PMC11577932
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S486301
Chronic Inflammation and Age-Related Hearing: Based on Mendelian Randomization
Abstract
Introduction: Age-related hearing loss (ARHL) is a degenerative condition that involves both peripheral and central auditory system pathologies. There is a close relationship between chronic inflammation and ARHL, but there is currently a lack of in-depth exploration of this relationship, particularly regarding causality.
Methods: Using age-appropriate mice for basic experiments to examine changes in central auditory nervous system inflammation, a cohort study was conducted to select relevant clinical data and observe inflammation changes in the elderly population with ARHL. Mendelian randomization was employed to investigate the causal relationship between chronic inflammation and ARHL.
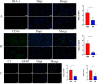
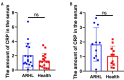
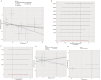
Results: Clinical results indicate that CRP levels in the ARHL group are significantly higher than those in the normal group. Chronic inflammation also occurs in the auditory centers. Mendelian randomization studies provide causal evidence that genetic chronic inflammation factors do not increase the risk of ARHL.
Discussion: This article provides reliable causal evidence of the relationship between chronic inflammation and ARHL, confirming the accumulation of inflammatory factors in the auditory center, which provides a basis for the prevention and treatment of ARHL and has a good prevention prospect. However, due to the differences of research objects, this study has limitations and needs further research.
Keywords: CRP; Mendelian randomization; TNF-α; age-related hearing loss; chronic inflammation.
© 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hearing intervention for decreasing risk of developing dementia in elders with mild cognitive impairment: study protocol of a multicenter randomized controlled trial for Chinese Hearing Solution for Improvement of Cognition in Elders (CHOICE).Trials. 2023 Nov 28;24(1):767. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07813-z. Trials. 2023. PMID: 38017543 Free PMC article.
-
No causal relationship serum lipids on age-related hearing loss based on Mendelian randomized evidence.Hear Res. 2024 Nov;453:109128. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2024.109128. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Hear Res. 2024. PMID: 39388794
-
Age-Related Hearing Loss Is Accompanied by Chronic Inflammation in the Cochlea and the Cochlear Nucleus.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 28;14:846804. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.846804. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35418849 Free PMC article.
-
Compensation in neuro-system related to age-related hearing loss.Acta Otolaryngol. 2024 Jan;144(1):30-34. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2023.2295400. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Acta Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38265951 Review.
-
Role of antioxidants in prevention of age-related hearing loss: a review of literature.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Apr;274(4):1821-1834. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4378-6. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 27858145 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

