Effect of Anchorage Modifications on the Efficacy of Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39569259
- PMCID: PMC11577497
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.72008
Effect of Anchorage Modifications on the Efficacy of Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Mini-implant-assisted rapid palatal expansion (MARPE) offers a non-surgical alternative for expanding the basal bone, increasing skeletal effects while minimizing undesirable dental side effects. This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluate the effectiveness of MARPE in terms of transverse skeletal development, dentoalveolar changes, and periodontal effects, with consideration of appliance design. A review was conducted across multiple databases, including PubMed, MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and Springer, covering studies published between 2005 and 2024. Randomized controlled trials involving MARPE, with specific attention to design variations (e.g., miniscrew type, number, diameter, length, position, and activation protocol), were selected. Transverse skeletal expansion, assessed via changes in the nasal width, was reported in six of seven studies, with an average increase ranging from 0.31 mm to 2.90 mm for MARPE, compared to 0.11 mm to 2.46 mm for conventional Hyrax expanders. Maxillary width expansion ranged from 2.89 mm to 9.08 mm with MARPE and from 2.59 mm to 8.51 mm with Hyrax. Periodontal changes were reported in six studies, although details were generally unclear. The use of four self-drilling miniscrews with once-daily activation over an extended period produced greater nasal width expansion, greater average skeletal expansion of the maxilla, and less dental inclination and dentoalveolar expansion compared to Hyrax. No significant differences were observed between short and long miniscrews, although wider miniscrews resulted in improved outcomes. The MARPE technique, especially when using a design with four self-drilling miniscrews and daily activation until the targeted expansion is reached, offers notable benefits compared to the conventional Hyrax appliance. This method improves both nasal and maxillary skeletal expansion, lessens dental inclination, and reduces negative effects relative to traditional approaches.
Keywords: maxillary expansion; miniscrews; orthodontic anchorage procedures; palatal expansion technique; randomized controlled trials.
Copyright © 2024, Villa-Obando et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
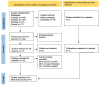
Figures





Similar articles
-
Skeletal and alveolar changes in conventional rapid palatal expansion (RPE) and miniscrew-assisted RPE (MARPE): a prospective randomized clinical trial using low-dose CBCT.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Apr 8;22(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02138-w. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 35395801 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment outcomes of 3D-printed custom and conventional mini-implant assisted rapid palatal expanders (MARPE).Prog Orthod. 2025 Aug 25;26(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40510-025-00576-0. Prog Orthod. 2025. PMID: 40853520 Free PMC article.
-
Degree and pattern of expansion of commercially available and custom-fabricated miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion systems in young adult patients: A retrospective comparative analysis.Int Orthod. 2025 Mar;23(1):100931. doi: 10.1016/j.ortho.2024.100931. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Int Orthod. 2025. PMID: 39454463
-
Efficacy of Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (MARPE) in late adolescents and adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Orthod. 2021 Jun 8;43(3):313-323. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjab005. Eur J Orthod. 2021. PMID: 33882127 Free PMC article.
-
Interest of miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion on the upper airway in growing patients: A systematic review.Int Orthod. 2022 Sep;20(3):100657. doi: 10.1016/j.ortho.2022.100657. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Int Orthod. 2022. PMID: 35752557
References
-
- Emerson C. Angell (1822-1903). Founding father of rapid maxillary expansion. Timms DJ. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9879204/ Dent Hist. 1997;32:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Dento-skeletal effects produced by rapid versus slow maxillary expansion using fixed jackscrew expanders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rutili V, Mrakic G, Nieri M, Franceschi D, Pierleoni F, Giuntini V, Franchi L. Eur J Orthod. 2021;43:301–312. - PubMed
-
- Effectiveness of miniscrew assisted rapid palatal expansion using cone beam computed tomography: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Siddhisaributr P, Khlongwanitchakul K, Anuwongnukroh N, Manopatanakul S, Viwattanatipa N. https://europepmc.org/article/PMC/PMC9117794. Korean J Orthod. 2022;52:182–200. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
