Insights into the role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in plant-virus interactions
- PMID: 39570081
- PMCID: PMC11784248
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01598-24
Insights into the role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in plant-virus interactions
Abstract
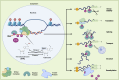
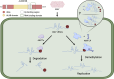
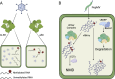
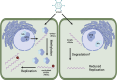
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a common and dynamic epitranscriptomic modification in eukaryotic RNAs, affecting stability, splicing, translation, and degradation. Recent technological advancements have revealed the complex nature of m6A modifications, highlighting their importance in plant and animal species. The m6A modification is a reversible process, with "writers" depositing methylation, "erasers" demethylating it, and "reader" proteins recognizing m6A and executing various biological functions. Studying the relationship between m6A methylation and viral infection is crucial. Animal viruses, including retroviruses, RNA viruses, and DNA viruses, often employ the host's m6A machinery to replicate or avoid immune responses. In plant viruses, host methyltransferases or demethylases can stabilize or degrade viral RNA, depending on the virus-host interaction. Additionally, viral infections can modify the host's m6A machinery, impacting the viral life cycle. This review examines the role of m6A modifications in plant viral pathogenesis, focussing on RNA viruses infecting crops like alfalfa, turnip, wheat, rice, and potato. Understanding the role of m6A in virus-host interactions can aid in studying plant viral disease development and discovering novel antiviral targets for crop protection. In this review, we summarize current information on m6A in RNA biology, focussing on its function in viral infections and plant-virus interactions.
Keywords: RNA modification; m6A; plant virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification: Emerging regulators in plant-virus interactions.Virology. 2025 Feb;603:110373. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2024.110373. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Virology. 2025. PMID: 39729962 Review.
-
Epitranscriptomic(N6-methyladenosine) Modification of Viral RNA and Virus-Host Interactions.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Nov 24;10:584283. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.584283. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33330128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of N6-methyladenosine with viruses and virally induced diseases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2020 Mar 1;25(6):1184-1201. doi: 10.2741/4852. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2020. Retraction in: Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Dec 29;28(12):369. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2812369. PMID: 32114429 Retracted. Review.
-
Association of N6-methyladenosine with viruses and related diseases.Virol J. 2019 Nov 11;16(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1236-3. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 31711514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Functions of N-methyladenosine (m6A) Modification on HIV-1 mRNA.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Jun;82(2):561-574. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01280-2. Epub 2024 May 16. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38753251 Review.
Cited by
-
M6A RNA modification: focusing on non-small cell lung cancer progression, therapeutic strategies and challenges.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 16;15:1622359. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1622359. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40740874 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen Y-S, Hao Y-J, Sun B-F, Sun H-Y, Li A, Ping X-L, Lai W-Y, Wang X, Ma H-L, Huang C-M, Yang Y, Huang N, Jiang G-B, Wang H-L, Zhou Q, Wang X-J, Zhao Y-L, Yang Y-G. 2016. Nuclear m(6)A reader YTHDC1 regulates mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 61:507–519. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2016.01.012 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

