Functional genetics reveals modulators of antimicrotubule drug sensitivity
- PMID: 39570287
- PMCID: PMC11590752
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202403065
Functional genetics reveals modulators of antimicrotubule drug sensitivity
Abstract
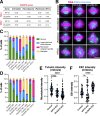
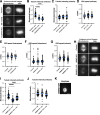
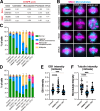
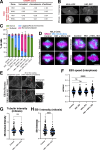
Microtubules play essential roles in diverse cellular processes and are important pharmacological targets for treating human disease. Here, we sought to identify cellular factors that modulate the sensitivity of cells to antimicrotubule drugs. We conducted a genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9-based functional genetics screen in human cells treated with the microtubule-destabilizing drug nocodazole or the microtubule-stabilizing drug paclitaxel. We further conducted a focused secondary screen to test drug sensitivity for ∼1,400 gene targets across two distinct human cell lines and to additionally test sensitivity to the KIF11 inhibitor, STLC. These screens defined gene targets whose loss enhances or suppresses sensitivity to antimicrotubule drugs. In addition to gene targets whose loss sensitized cells to multiple compounds, we observed cases of differential sensitivity to specific compounds and differing requirements between cell lines. Our downstream molecular analysis further revealed additional roles for established microtubule-associated proteins and identified new players in microtubule function.
© 2024 Su et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures


Update of
-
Functional genetics reveals modulators of anti-microtubule drug sensitivity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 13:2024.03.12.584469. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.12.584469. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Cell Biol. 2025 Feb 3;224(2):e202403065. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202403065. PMID: 38559203 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ashoti, A., Limone F., van Kranenburg M., Alemany A., Baak M., Vivié J., Piccioni F., Dijkers P.F., Creyghton M., Eggan K., and Geijsen N.. 2022. Considerations and practical implications of performing a phenotypic CRISPR/Cas survival screen. PLoS One. 17:e0263262. 10.1371/journal.pone.0263262 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

