ACK1 and BRK non-receptor tyrosine kinase deficiencies are associated with familial systemic lupus and involved in efferocytosis
- PMID: 39570652
- PMCID: PMC11581429
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.96085
ACK1 and BRK non-receptor tyrosine kinase deficiencies are associated with familial systemic lupus and involved in efferocytosis
Abstract
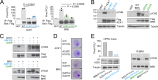
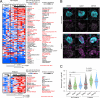
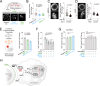
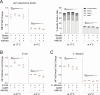
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease, the pathophysiology and genetic basis of which are incompletely understood. Using a forward genetic screen in multiplex families with SLE, we identified an association between SLE and compound heterozygous deleterious variants in the non-receptor tyrosine kinases (NRTKs) ACK1 and BRK. Experimental blockade of ACK1 or BRK increased circulating autoantibodies in vivo in mice and exacerbated glomerular IgG deposits in an SLE mouse model. Mechanistically, NRTKs regulate activation, migration, and proliferation of immune cells. We found that the patients' ACK1 and BRK variants impair efferocytosis, the MERTK-mediated anti-inflammatory response to apoptotic cells, in human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived macrophages, which may contribute to SLE pathogenesis. Overall, our data suggest that ACK1 and BRK deficiencies are associated with human SLE and impair efferocytosis in macrophages.
Keywords: ACK1; BRK; genetic diseases; genetics; genomics; human; immunology; inflammation; mouse; systemic lupus.
© 2024, Guillet, Lazarov et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SG, TL, NJ, BB, MT, BC, TZ, CN, RB, HY, FR, RF, SD, DI, DD, NL, OE, AV, NS, LA, SN, MH, WM, JC, FG No competing interests declared
Figures
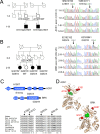






Update of
-
ACK1 and BRK non-receptor tyrosine kinase deficiencies are associated with familial systemic lupus and involved in efferocytosis.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 5:2024.02.15.24302255. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.15.24302255. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Nov 21;13:RP96085. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96085. PMID: 38883731 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Alarcón-Segovia D, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, Cardiel MH, Caeiro F, Massardo L, Villa AR, Pons-Estel BA, Grupo Latinoamericano de Estudio del Lupus Eritematoso Familial aggregation of systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune diseases in 1,177 lupus patients from the GLADEL cohort. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2005;52:1138–1147. doi: 10.1002/art.20999. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al Mayouf SM, Sunker A, Abdwani R, Abrawi SA, Almurshedi F, Alhashmi N, Al Sonbul A, Sewairi W, Qari A, Abdallah E, Al-Owain M, Al Motywee S, Al-Rayes H, Hashem M, Khalak H, Al-Jebali L, Alkuraya FS. Loss-of-function variant in DNASE1L3 causes a familial form of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nature Genetics. 2011;43:1186–1188. doi: 10.1038/ng.975. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 AI124349/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01AI124349-03/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- JPMJCR14M4/Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology
- P30CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01AI130345-01/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- R01 AI130345/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA058530/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI087644/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- DEA20140630127/Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale
- CA58530/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI164424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Annee Recherche/Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris
- No. 15H05785/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research
- Fellowship/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 AI087644/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

