Gentiopicroside-Induced gastric cancer necroptosis via the HIF-1 signaling pathway: A study involving molecular docking and experimental validation
- PMID: 39570876
- PMCID: PMC11581292
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311152
Gentiopicroside-Induced gastric cancer necroptosis via the HIF-1 signaling pathway: A study involving molecular docking and experimental validation
Abstract
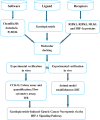
Objectives: Gentiopicroside is an effective treatment for several types of cancer, inducing numerous forms of programmed cancer cell death. However, there are few investigations into the role of necroptosis. By utilizing molecular docking, and experimental validation, this study aims to investigate whether gentiopicroside elicits necroptosis in gastric cancer.
Methods: Using software PyMOL and AutoDock, gentiopicroside was docked with RIPK1, RIPK3, MLKL and HIF-1α proteins. And a cell study was performed based on SGC7901 cells. The necroptosis-related proteins and HIF-1 signaling pathways were explored using western blot (WB) analysis. Finally, an animal study was performed to test the inhibitory effect in vivo.
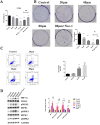
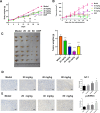
Results: Docking studies indicated that the docking energies of gentiopicroside to necroptosis-related proteins and necroptosis-characteristic proteins are all below -5 kcal/mol. Additionally, gentiopicroside cells reduce gastric cancer viability and inhibit proliferation. Results from the animal experiments indicated that gentiopicroside inhibits the growth of the gastric cancer xenograft tumor. Western blot and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining demonstrated that gentiopicroside higher p-receptor-interacting protein kinase 3(p-RIPK3) levels in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: The findings of this study revealed that necroptosis is involved in the inhibitory effect of gentiopicroside toward gastric cancer.
Copyright: © 2024 Xiong et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Induction of necroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by miR‑10b‑5p through modulation of the PKP3/RIPK3/MLKL cascade.Oncol Rep. 2025 May;53(5):56. doi: 10.3892/or.2025.8889. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40116080 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the Potential Mechanism of Gentiopicroside Against Gastric Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Nov 23;14:5109-5118. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S270757. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 33262572 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin ameliorates necroptosis in Glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head via RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL pathway based on network pharmacology analysis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023 Jun 18;661:108-118. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.04.023. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37099894
-
20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 induced the necroptosis of prostate cancer cells via ROS overproduction.Neoplasma. 2025 Apr;72(1-2):48-58. doi: 10.4149/neo_2025_240925N402. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Neoplasma. 2025. PMID: 40162506
-
RIPK3 signaling and its role in the pathogenesis of cancers.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(23):7199-7217. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03947-y. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34654937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

