Lewy pathology formation in patient-derived GBA1 Parkinson's disease midbrain organoids
- PMID: 39570889
- PMCID: PMC11967528
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awae365
Lewy pathology formation in patient-derived GBA1 Parkinson's disease midbrain organoids
Abstract
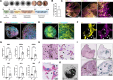
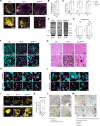
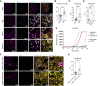
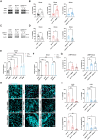
Fibrillary aggregation of α-synuclein in Lewy body inclusions and nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuron degeneration define Parkinson's disease neuropathology. Mutations in GBA1, encoding glucocerebrosidase, are the most frequent genetic risk factor for Parkinson's disease. However, the lack of reliable experimental models able to reproduce key neuropathological signatures has hampered clarification of the link between mutant glucocerebrosidase and Parkinson's disease pathology. Here, we describe an innovative protocol for the generation of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived midbrain organoids containing dopaminergic neurons with nigral identity that reproduce characteristics of advanced maturation. When applied to patients with GBA1-related Parkinson's disease, this method enabled the differentiation of midbrain organoids recapitulating dopaminergic neuron loss and fundamental features of Lewy pathology observed in human brains, including the generation of α-synuclein fibrillary aggregates with seeding activity that also propagate pathology in healthy control organoids. Concurrently, we found that the retention of mutant glucocerebrosidase in the endoplasmic reticulum and increased levels of its substrate, glucosylceramide, are determinants of α-synuclein aggregation into Lewy body-like inclusions, and the reduction of glucocerebrosidase activity accelerated α-synuclein pathology by promoting fibrillary α-synuclein deposition. Finally, we demonstrated the efficacy of ambroxol and GZ667161 (two modulators of the glucocerebrosidase pathway in clinical development for the treatment of GBA1-related Parkinson's disease) in reducing α-synuclein pathology in this model, supporting the use of midbrain organoids as a relevant preclinical platform for investigational drug screening.
Keywords: GBA1; Lewy bodies; Parkinson’s disease; ambroxol; glucocerebrosidase; midbrain organoids.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests. S.P.S. is an employee and stockholder of Sanofi. He provided the molecule GZ667161 that was tested in midbrain organoids. To avoid potential biases, this author was excluded from experiments and analysis of data concerning use of GZ667161 in midbrain organoids. No research funding was obtained from any company for the present study.
Figures

References
-
- Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Del Tredici K, Braak H. 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013;9:13–24. - PubMed
-
- Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M. α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature. 1997;388:839–840. - PubMed
-
- Shahmoradian SH, Lewis AJ, Genoud C, et al. Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:1099–1109. - PubMed

