Single-cell sequencing reveals transcriptional dynamics regulated by ERα in mouse ovaries
- PMID: 39570927
- PMCID: PMC11581351
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313867
Single-cell sequencing reveals transcriptional dynamics regulated by ERα in mouse ovaries
Abstract
Context: Estrogen receptor α (ERα) is a key regulator of reproductive function, particularly in ovarian development and function, yet the specifics of its role at the molecular level remain unclear.
Aims: The study aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of ERα-regulated transcriptional dynamics in ovarian cells using ERα knockout (αERKO) mice created via CRISPR/Cas9.
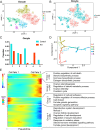
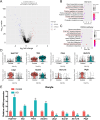
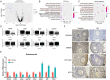
Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was used to compare transcriptomes from individual ovarian cells in both wild type and αERKO mice. Bioinformatics analyses identified distinct cell populations and their transcriptional profiles post ERα deletion.
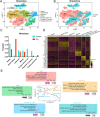
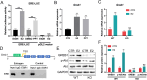
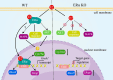
Key results: Distinct oocyte and granulosa cell populations were identified, with ERα deletion disrupting the regulation of genes linked to ovarian infertility, the ovulation cycle, and steroidogenesis. Greb1 expression in granulosa cells was found to be ERα-dependent.
Conclusions: ERα deletion significantly alters the transcriptional landscape of ovarian cells, affecting genes and pathways central to ovarian function and the ovulation process.
Implications: The findings provide an in-depth, single-cell view of ERα's role in the reproductive system, offering insights that may lead to novel treatments for ovarian disorders.
Copyright: © 2024 Hu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prevention of the polycystic ovarian phenotype and characterization of ovulatory capacity in the estrogen receptor-alpha knockout mouse.Endocrinology. 1999 Dec;140(12):5855-65. doi: 10.1210/endo.140.12.7222. Endocrinology. 1999. PMID: 10579351
-
Luteinizing Hormone Receptor Mutation (LHRN316S) Causes Abnormal Follicular Development Revealed by Follicle Single-Cell Analysis and CRISPR/Cas9.Interdiscip Sci. 2024 Dec;16(4):976-989. doi: 10.1007/s12539-024-00646-7. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Interdiscip Sci. 2024. PMID: 39150470 Free PMC article.
-
IGF-1 gene expression is differentially regulated by estrogen receptors α and β in mouse endometrial stromal cells and ovarian granulosa cells.J Reprod Dev. 2014;60(3):216-23. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2013-085. Epub 2014 Mar 25. J Reprod Dev. 2014. PMID: 24670778 Free PMC article.
-
ERβ Regulation of Gonadotropin Responses during Folliculogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 26;22(19):10348. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910348. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Single-Cell RNA Sequencing in Ovarian Development.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 27;13(1):47. doi: 10.3390/biom13010047. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36671432 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acephate Exposure Induces Transgenerational Ovarian Developmental Toxicity by Altering the Expression of Follicular Growth Markers in Female Rats.Biology (Basel). 2024 Dec 20;13(12):1075. doi: 10.3390/biology13121075. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765742 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

