The Chemistry of Phytoplankton
- PMID: 39571071
- PMCID: PMC11638913
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00177
The Chemistry of Phytoplankton
Abstract
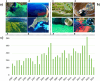
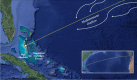
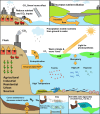
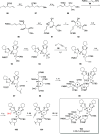
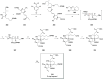
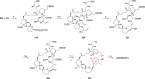
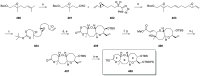
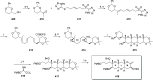
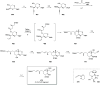
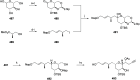
Phytoplankton have a high potential for CO2 capture and conversion. Besides being a vital food source at the base of oceanic and freshwater food webs, microalgae provide a critical platform for producing chemicals and consumer products. Enhanced nutrient levels, elevated CO2, and rising temperatures increase the frequency of algal blooms, which often have negative effects such as fish mortalities, loss of flora and fauna, and the production of algal toxins. Harmful algal blooms (HABs) produce toxins that pose major challenges to water quality, ecosystem function, human health, tourism, and the food web. These toxins have complex chemical structures and possess a wide range of biological properties with potential applications as new therapeutics. This review presents a balanced and comprehensive assessment of the roles of algal blooms in generating fixed carbon for the food chain, sequestering carbon, and their unique secondary metabolites. The structural complexity of these metabolites has had an unprecedented impact on structure elucidation technologies and total synthesis, which are highlighted throughout this review. In addition, the influence of biogeochemical environmental perturbations on algal blooms and their influence on biospheric environments is discussed. Lastly, we summarize work on management strategies and technologies for the control and treatment of HABs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






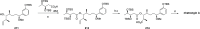









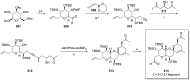

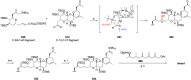

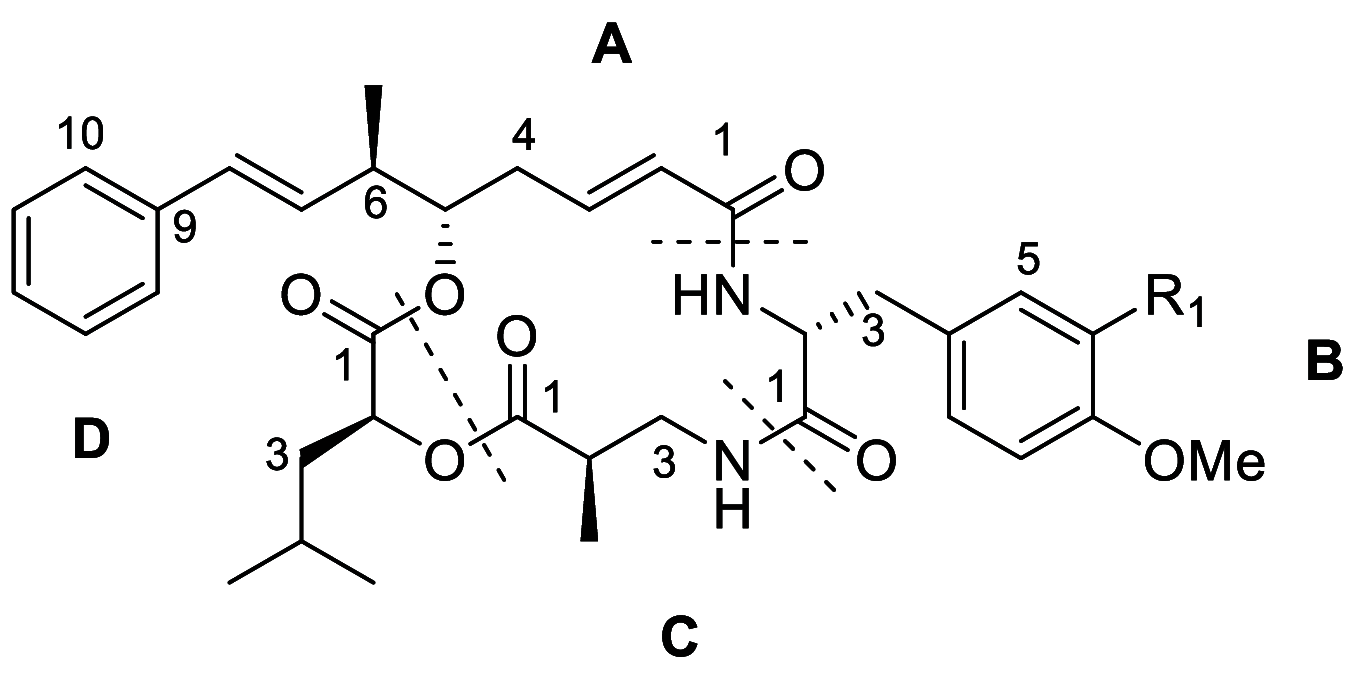
References
-
- Schopf J. W.The fossil record: tracing the roots of the cyanobacterial lineage. In The Ecology of Cyanobacteria. Whitton B.A., Potts M., eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 2000, pp.13–35.10.1007/0-306-46855-7_2 - DOI
-
- Krause-Jensen D.; Duarte C. Substantial role of macroalgae in marine carbon sequestration. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 737–742. 10.1038/ngeo2790. - DOI
-
- Prasad R.; Gupta S. K.; Shabnam N.; Oliveira C. Y. B.; Nema A. K.; Ansari F. A.; Bux F. Role of microalgae in global CO2 sequestration: Physiological mechanism, recent development, challenges, and future prospective. Sustainability 2021, 13 (23), 13061.10.3390/su132313061. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

