A Mindfulness-Based Lifestyle Intervention for Dementia Risk Reduction: Protocol for the My Healthy Brain Feasibility Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39571150
- PMCID: PMC11621724
- DOI: 10.2196/64149
A Mindfulness-Based Lifestyle Intervention for Dementia Risk Reduction: Protocol for the My Healthy Brain Feasibility Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
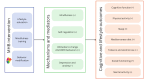
Background: Lifestyle behavior change and mindfulness have direct and synergistic effects on cognitive functioning and may prevent Alzheimer disease and Alzheimer disease-related dementias (AD/ADRD). We are iteratively developing and testing My Healthy Brain (MHB), the first mindfulness-based lifestyle group program targeting AD/ADRD risk factors in older adults with subjective cognitive decline. Our pilot studies (National Institutes of Health [NIH] stage 1A) have shown that MHB is feasible, acceptable, and associated with improvement in lifestyle behavior and cognitive outcomes.
Objective: We will compare the feasibility of MHB versus an education control (health enhancement program [HEP]) in 50 older adults (aged ≥60 y) with subjective cognitive decline and AD/ADRD risk factors. In an NIH stage 1B randomized controlled trial (RCT), we will evaluate feasibility benchmarks, improvements in cognitive and lifestyle outcomes, and engagement of hypothesized mechanisms.
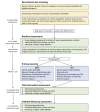
Methods: We are recruiting through clinics, flyers, web-based research platforms, and community partnerships. Participants are randomized to MHB or the HEP, both delivered in telehealth groups over 8 weeks. MHB participants learn behavior modification and mindfulness skills to achieve individualized lifestyle goals. HEP participants receive lifestyle education and group support. Assessments are repeated after the intervention and at a 6-month follow-up. Our primary outcomes are feasibility, acceptability, appropriateness, credibility, satisfaction, and fidelity benchmarks. The secondary outcomes are cognitive function and lifestyle (physical activity, sleep, nutrition, alcohol and tobacco use, and mental and social activity) behaviors. Data analyses will include the proportion of MHB and HEP participants who meet each benchmark (primary outcome) and paired samples 2-tailed t tests, Cohen d effect sizes, and the minimal clinically important difference for each measure (secondary outcomes).
Results: Recruitment began in January 2024. We received 225 inquiries. Of these 225 individuals, 40 (17.8%) were eligible. Of the 40 eligible participants, 21 (52.5%) were enrolled in 2 group cohorts, 17 (42.5%) were on hold for future group cohorts, and 2 (5%) withdrew before enrollment. All participants have completed before the intervention assessments. All cohort 1 participants (9/21, 43%) have completed either MHB or the HEP (≥6 of 8 sessions) and after the intervention assessments. The intervention for cohort 2 (12/21, 57%) is ongoing. Adherence rates for the Garmin Vivosmart 5 (128/147, 87.1% weeks) and daily surveys (105/122, 86.1% weeks) are high. No enrolled participants have dropped out. Enrollment is projected to be completed by December 2024.
Conclusions: The RCT will inform the development of a larger efficacy RCT (NIH stage 2) of MHB versus the HEP in a more diverse sample of older adults, testing mechanisms of improvements through theoretically driven mediators and moderators. The integration of mindfulness with lifestyle behavior change in MHB has the potential to be an effective and sustainable approach for increasing the uptake of AD/ADRD risk reduction strategies among older adults.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT05934136; https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05934136.
International registered report identifier (irrid): DERR1-10.2196/64149.
Keywords: brain health; cognitive decline; digital health; lifestyle; mind-body therapies; mindfulness; randomized clinical trial; telemedicine.
©Ryan A Mace, Makenna E Law, Joshua E Cohen, Christine S Ritchie, Olivia I Okereke, Bettina B Hoeppner, Judson A Brewer, Stephen J Bartels, Ana-Maria Vranceanu, My Healthy Brain Team. Originally published in JMIR Research Protocols (https://www.researchprotocols.org), 21.11.2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Grand JH, Caspar S, Macdonald SW. Clinical features and multidisciplinary approaches to dementia care. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2011;4:125–47. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S17773. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/21655340 jmdh-4-125 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cattaneo G, Bartrés-Faz D, Morris TP, Sánchez JS, Macià D, Tarrero C, Tormos JM, Pascual-Leone A. The Barcelona Brain Health Initiative: a cohort study to define and promote determinants of brain health. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:321. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00321. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/30405394 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gorelick PB, Furie KL, Iadecola C, Smith EE, Waddy SP, Lloyd-Jones DM, Bae HJ, Bauman MA, Dichgans M, Duncan PW, Girgus M, Howard VJ, Lazar RM, Seshadri S, Testai FD, van Gaal S, Yaffe K, Wasiak H, Zerna C, American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Defining optimal brain health in adults: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2017 Oct;48(10):e284–303. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000148. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/28883125 STR.0000000000000148 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gelfo F, Mandolesi L, Serra L, Sorrentino G, Caltagirone C. The neuroprotective effects of experience on cognitive functions: evidence from animal studies on the neurobiological bases of brain reserve. Neuroscience. 2018 Feb 01;370:218–35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.07.065.S0306-4522(17)30551-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer's Association. [2024-04-29]. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/facts-figures . - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

