The 7-Methylguanosine (m7G) methylation METTL1 acts as a potential biomarker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression
- PMID: 39571491
- PMCID: PMC11617297
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102202
The 7-Methylguanosine (m7G) methylation METTL1 acts as a potential biomarker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression
Abstract
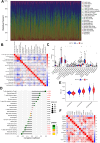
Background: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most common subtype of renal cancer. 7-Methylguanosine (m7G), one of the most prevalent RNA modifications, has been reported to play an important role in ccRCC progression; however, the specific regulators of m7G modification that are involved in this function remain unclear. This study aimed to explore the correlation between regulators of m7G methylation and ccRCC progression using unsupervised machine learning methods.
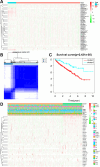
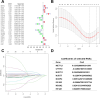
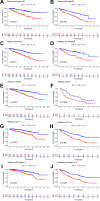
Methods: Transcriptome and clinical data of ccRCC were retrieved from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database to identify differentially expressed m7G-related genes associated with the overall survival of patients with ccRCC. To construct and validate a prognostic risk model, TCGA dataset samples were divided into training and test sets. A multiple-gene risk signature was constructed using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator Cox regression analysis, and its prognostic significance was assessed using Cox regression and survival analyses. Finally, immunohistochemistry was performed to verify the prognostic significance of this signature.
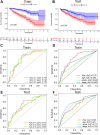
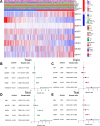
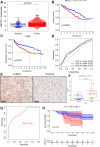
Results: In total, 537 patients with ccRCC were included in this study. We found that 26 m7G RNA methylation regulators that were significantly differentially expressed. Univariate and multifactorial Cox regression analyses revealed that METTL1 expression was associated with ccRCC progression.
Conclusions: METTL1 associated with m7G may serve as a potential biomarker for ccRCC prognosis and diagnosis. Moreover, it may affect the prognosis of ccRCC by regulating the tumor immune microenvironment, providing a potential therapeutic target for immunotherapy. These results provide a new perspective on the role of M7G-related RNAs in ccRCC pathogenesis.
Keywords: 7-methylguanosine (m7G); Clear cell renal cell carcinoma; METTL1; Prognosis; Tumor immune microenvironment.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2019;69:363–385. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Aweys H, Lewis D, Sheriff M, Rabbani RD, Lapitan P, Sanchez E, et al. Renal cell cancer – insights in drug resistance mechanisms. Anticancer Res. 2023;43:4781–4792. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

