ELF3 Overexpression Contributes to the Malignant Transformation of HPV16 E6/E7-Immortalized Keratinocytes by Promoting CCNE2 Expression
- PMID: 39572025
- PMCID: PMC11733543
- DOI: 10.4014/jmb.2408.08041
ELF3 Overexpression Contributes to the Malignant Transformation of HPV16 E6/E7-Immortalized Keratinocytes by Promoting CCNE2 Expression
Abstract
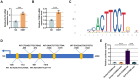
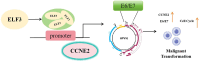
Current cancer burden caused by persistent infection with human papillomaviruse genotype 16 (HPV16) cannot be ignored. The related mechanisms of oncoproteins E6 and E7 from HPV16 on keratinocyte malignant transformation need to be further elucidated. GSE3292 dataset analysis revealed the upregulation of ETS transcription factor 3 (ELF3) and cyclin E2 (CCNE2). To verify whether there is an interaction between ELF3 and CCNE2, E74 like ELF3 and CCNE2 expression profiles as well as their putative binding sites were analyzed using bioinformatics. Retroviruses encoding HPV16 E6 and E7 genes were used to induce immortalization of human foreskin keratinocytes (HFKs) in vitro. Dual luciferase reporters assay was used to verify the binding of ELF3 and CCNE2. The effect of ELF3 on the immortalized cells was investigated using CCK-8 assay, cell cycle analysis and western blot. ELF3 and CCNE2 presented overexpression patterns in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. HPV16 E6/E7-expressing HFKs showed enhanced viability, accelerated cell cycle as well as upregulated ELF3 and CCNE2. ELF3 overexpression enhanced the activity of CCNE2 promoter. ELF3 silencing reduced viability, induced cell cycle arrest and suppressed expressions of CCNE2, E6 and E7 in HPV16 E6/E7-expressing HFKs. Downregulation of ELF3 played an inhibiting role in the malignant transformation of HPV16 E6/E7-immortalized HFKs by decreasing CCNE2 expression.
Keywords: E74 like ETS transcription factor 3; Human papillomavirus genotype 16 E6/E7; cyclin E2; keratinocytes; malignant transformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cytoplasmic poly(A) binding proteins regulate telomerase activity and cell growth in human papillomavirus type 16 E6-expressing keratinocytes.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(24):12934-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01377-10. Epub 2010 Oct 13. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20943973 Free PMC article.
-
Different HPV16 E6/E7 oncogene expression patterns in epithelia reconstructed from HPV16-immortalized human endocervical cells and genital keratinocytes.Oncogene. 1997 Nov 13;15(20):2399-408. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201425. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9395236
-
Recombinant adenoviruses expressing HPV16/18 E7 upregulate the HDAC6 and DNMT3B genes in C33A cells.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Oct 1;14:1459572. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1459572. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39411320 Free PMC article.
-
HPV DNA, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16INK4a detection in head and neck cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Nov;15(12):1319-31. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70471-1. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25439690
-
High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Oncogenic E6/E7 mRNAs Splicing Regulation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jun 27;12:929666. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.929666. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35832386 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

