mTORC1, the maestro of cell metabolism and growth
- PMID: 39572234
- PMCID: PMC11789495
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.352084.124
mTORC1, the maestro of cell metabolism and growth
Abstract
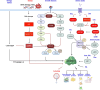
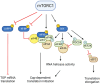
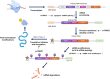
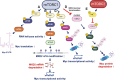
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway senses and integrates various environmental and intracellular cues to regulate cell growth and proliferation. As a key conductor of the balance between anabolic and catabolic processes, mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) orchestrates the symphonic regulation of glycolysis, nucleic acid and lipid metabolism, protein translation and degradation, and gene expression. Dysregulation of the mTOR pathway is linked to numerous human diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, obesity, diabetes, and aging. This review provides an in-depth understanding of how nutrients and growth signals are coordinated to influence mTOR signaling and the extensive metabolic rewiring under its command. Additionally, we discuss the use of mTORC1 inhibitors in various aging-associated metabolic diseases and the current and future potential for targeting mTOR in clinical settings. By deciphering the complex landscape of mTORC1 signaling, this review aims to inform novel therapeutic strategies and provide a road map for future research endeavors in this dynamic and rapidly evolving field.
Keywords: cancer; cellular signaling; mT; mTOR complex 1; mTORC1.
© 2025 He et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
