Inpatient Burden of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection and Influenza in Children Younger Than 5 Years in Japan, 2011-2022: A Database Study
- PMID: 39572401
- PMCID: PMC11581829
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.70045
Inpatient Burden of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection and Influenza in Children Younger Than 5 Years in Japan, 2011-2022: A Database Study
Abstract
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and influenza virus are major viral etiologies of pediatric lower respiratory tract infection, but comparative data on inpatient burden are lacking.
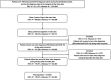
Methods: Using a large-scale health claims database in Japan, we identified patients under 5 years of age with a confirmed RSV or influenza diagnosis as an outpatient or inpatient between 2011 and 2022. Hospitalization rate, inpatient characteristics, various in-hospital outcomes/complications, and healthcare resource utilization were described.
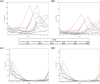
Results: A total of 176,911 RSV-confirmed outpatients, 153,383 influenza-confirmed outpatients, 90,413 RSV-confirmed hospitalizations, and 11,186 influenza-confirmed hospitalizations were identified. Among outpatients, 24.7% of RSV infection and 2.8% of influenza cases required hospitalization within 1 week. There was no co-morbidities/prematurity for 95.0% of RSV hospitalizations and 96.5% of influenza hospitalizations. Proportions of in-hospital outcomes/complications were (RSV infection vs. influenza): oxygen use 47.6% vs. 14.8%, mechanical ventilation 2.1% vs. 0.7%, pneumonia 33.6% vs. 12.8%, otitis media 7.7% vs. 2.3%, febrile seizure 1.5% vs. 34.4%, encephalitis/encephalopathy 0.1% vs. 0.5%, myocarditis < 0.1% vs. 0.6%, antibiotics prescription 48.0% vs. 24.4%. The mean inpatient stay was 6.1 vs. 4.3 days at direct medical costs of 435,744 vs. 315,809 JPY/patient. These trends held true in age-stratified data. In-hospital death occurred in 31 RSV infection and 6 influenza cases.
Conclusions: Although both infections resulted in substantial burden, RSV infection led to more frequent hospitalizations, worse in-hospital outcomes, longer inpatient stays, higher medical costs, and more frequent antibiotics prescription compared to influenza. Most RSV hospitalizations occurred among healthy term children, emphasizing the need for prevention measures in all children.
Keywords: Japan; hospitalization; influenza; pediatrics; respiratory syncytial virus infections.
© 2024 The Author(s). Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Takeshi Arashiro is a Sanofi employee and a cooperative researcher at the National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Japan. Rolf Kramer, Jing Jin, and Munehide Kano are Sanofi employees. Fangyuan Wang is a Syneos Health employee. Isao Miyairi received honoraria from Sanofi for lectures and advisory committees.
Figures
References
-
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases . Weekly Infectious Disease Report. https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/ja/idwr.html. Accessed December 23, 2023. (In Japanese)
-
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases . Influenza Epidemiological Information. https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/ja/diseases/a/flu.html. Accessed December 23, 2023. (In Japanese)
-
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases , “RS Virus Infections 2018‐2021,” Infectious Agents Surveillance Report. 43, no. 4 (2022): 79–81 (In Japanese).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

