In-context learning enables multimodal large language models to classify cancer pathology images
- PMID: 39572531
- PMCID: PMC11582649
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51465-9
In-context learning enables multimodal large language models to classify cancer pathology images
Abstract
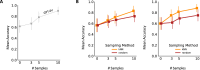
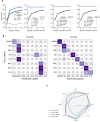
Medical image classification requires labeled, task-specific datasets which are used to train deep learning networks de novo, or to fine-tune foundation models. However, this process is computationally and technically demanding. In language processing, in-context learning provides an alternative, where models learn from within prompts, bypassing the need for parameter updates. Yet, in-context learning remains underexplored in medical image analysis. Here, we systematically evaluate the model Generative Pretrained Transformer 4 with Vision capabilities (GPT-4V) on cancer image processing with in-context learning on three cancer histopathology tasks of high importance: Classification of tissue subtypes in colorectal cancer, colon polyp subtyping and breast tumor detection in lymph node sections. Our results show that in-context learning is sufficient to match or even outperform specialized neural networks trained for particular tasks, while only requiring a minimal number of samples. In summary, this study demonstrates that large vision language models trained on non-domain specific data can be applied out-of-the box to solve medical image-processing tasks in histopathology. This democratizes access of generalist AI models to medical experts without technical background especially for areas where annotated data is scarce.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare the following competing interests. O.S.M.E.N. holds shares in StratifAI GmbH. J.N.K. declares consulting services for Owkin, France; DoMore Diagnostics, Norway; Panakeia, UK, and Scailyte, Basel, Switzerland; furthermore J.N.K. holds shares in Kather Consulting, Dresden, Germany; and StratifAI GmbH, Dresden, Germany, and has received honoraria for lectures and advisory board participation by AstraZeneca, Bayer, Eisai, MSD, BMS, Roche, Pfizer and Fresenius. D.T. received honoraria for lectures by Bayer and holds shares in StratifAI GmbH, Germany. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Gilbert, S., Harvey, H., Melvin, T., Vollebregt, E. & Wicks, P. Large language model AI chatbots require approval as medical devices. Nat. Med.29, 2396–2398 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Shmatko, A., Ghaffari Laleh, N., Gerstung, M. & Kather, J. N. Artificial intelligence in histopathology: enhancing cancer research and clinical oncology. Nat. Cancer3, 1026–1038 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

