Functional annotation of the Hippo pathway somatic mutations in human cancers
- PMID: 39572544
- PMCID: PMC11582751
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54480-y
Functional annotation of the Hippo pathway somatic mutations in human cancers
Abstract
The Hippo pathway is commonly altered in cancer initiation and progression; however, exactly how this pathway becomes dysregulated to promote human cancer development remains unclear. Here we analyze the Hippo somatic mutations in the human cancer genome and functionally annotate their roles in targeting the Hippo pathway. We identify a total of 85 loss-of-function (LOF) missense mutations for Hippo pathway genes and elucidate their underlying mechanisms. Interestingly, we reveal zinc-finger domain as an integral structure for MOB1 function, whose LOF mutations in head and neck cancer promote tumor growth. Moreover, the schwannoma/meningioma-derived NF2 LOF mutations not only inhibit its tumor suppressive function in the Hippo pathway, but also gain an oncogenic role for NF2 by activating the VANGL-JNK pathway. Collectively, our study not only offers a rich somatic mutation resource for investigating the Hippo pathway in human cancers, but also provides a molecular basis for Hippo-based cancer therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: K.-L.G. is a co-founder of and holds an equity interest in Vivace Therapeutics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

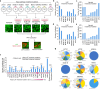

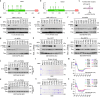
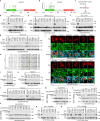
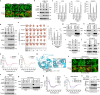

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54CA217378/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R35GM130367/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- 32370766/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- R01 GM143233/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM126048/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- RSG-18-009-01-CCG/American Cancer Society (American Cancer Society, Inc.)
- R01 GM126048/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA217378/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA062203/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01GM143233/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- P30 CA062203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM130367/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

