High refresh rate display for natural monocular viewing in AOSLO psychophysics experiments
- PMID: 39573257
- PMCID: PMC11595291
- DOI: 10.1364/OE.529199
High refresh rate display for natural monocular viewing in AOSLO psychophysics experiments
Abstract
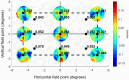
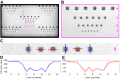
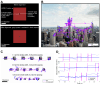
By combining an external display operating at 360 frames per second with an adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscope (AOSLO) for human foveal imaging, we demonstrate color stimulus delivery at high spatial and temporal resolution in AOSLO psychophysics experiments. A custom pupil relay enables viewing of the stimulus through a 3-mm effective pupil diameter and provides refractive error correction from -8 to +4 diopters. Performance of the assembled and aligned pupil relay was validated by measuring the wavefront error across the field of view and correction range, and the as-built Strehl ratio was 0.64 or better. High-acuity stimuli were rendered on the external display and imaged through the pupil relay to demonstrate that spatial frequencies up to 54 cycles per degree, corresponding to 20/11 visual acuity, are resolved. The completed external display was then used to render fixation markers across the field of view of the monitor, and a continuous retinal montage spanning 9.4 by 5.4 degrees of visual angle was acquired with the AOSLO. We conducted eye-tracking experiments during free-viewing and high-acuity tasks with polychromatic images presented on the external display. Sub-arcminute eye position uncertainty was achieved over a 1.5 by 1.5-degree trackable range, enabling precise localization of the line of sight on the stimulus while simultaneously imaging the fine structure of the human central fovea. This high refresh rate display overcomes the temporal, spectral, and field of view limitations of AOSLO-based stimulus presentation, enabling natural monocular viewing of stimuli in psychophysics experiments conducted with AOSLO.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Figures





Update of
-
High refresh rate display for natural monocular viewing in AOSLO psychophysics experiments.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 31:2024.05.26.595808. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.26.595808. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Opt Express. 2024 Aug 26;32(18):31142-31161. doi: 10.1364/OE.529199. PMID: 38854135 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
High refresh rate display for natural monocular viewing in AOSLO psychophysics experiments.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 31:2024.05.26.595808. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.26.595808. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Opt Express. 2024 Aug 26;32(18):31142-31161. doi: 10.1364/OE.529199. PMID: 38854135 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Cone Density Changes After Repeated Low-Level Red Light Treatment in Children With Myopia.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2025 Jun 1;143(6):480-488. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2025.0835. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40272813 Free PMC article.
-
Community screening for visual impairment in older people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 20;2(2):CD001054. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001054.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29460275 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Imaging of the Parafoveal Cone Mosaic in Congenital Achromatopsia.Ophthalmol Sci. 2025 Mar 14;5(4):100765. doi: 10.1016/j.xops.2025.100765. eCollection 2025 Jul-Aug. Ophthalmol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40291393 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for diabetic macular oedema: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 22;6(6):CD007419. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007419.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 16;10:CD007419. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007419.pub6. PMID: 28639415 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Asymmetric Activation of Retinal ON and OFF Pathways by AOSLO Raster-Scanned Visual Stimuli.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 17:2024.12.17.628952. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.17.628952. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Biomed Opt Express. 2025 Jun 09;16(7):2663-2691. doi: 10.1364/BOE.566008. PMID: 39763934 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Asymmetric activation of retinal ON and OFF pathways by AOSLO raster-scanned visual stimuli.Biomed Opt Express. 2025 Jun 9;16(7):2663-2691. doi: 10.1364/BOE.566008. eCollection 2025 Jul 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2025. PMID: 40677827 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

