Role of transglutaminase 2 in promoting biglycan synthesis in idiopathic gingival fibromatosis
- PMID: 39574071
- PMCID: PMC11583685
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-05211-8
Role of transglutaminase 2 in promoting biglycan synthesis in idiopathic gingival fibromatosis
Abstract
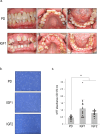
Background: This study aimed to elucidate the pathogenesis of idiopathic gingival fibromatosis (IGF).
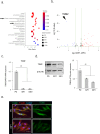
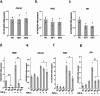
Methods: Human gingival fibroblasts (hGFs) were isolated from patients with IGF and periodontitis. Differential gene expression in the hGFs was analyzed using RNA sequencing. Extracellular matrix-related gene expression in the hGFs was analyzed. The effect of specific protein (SP)1 inhibitor or recombinant human transglutaminase 2 (rh-TGM2) on biglycan (BGN) expression in hGFs was also determined.
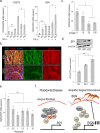
Results: RNA sequencing showed that TGM2 expression was downregulated and BGN mRNA expression was upregulated in patients with IGF relative to periodontitis. rh-TGM2 stimulation of hGFs in patients with IGF significantly reduced BGN expression. SP1 inhibitors downregulated BGN expression in the hGFs.
Conclusion: BGN upregulation via SP1 causes TGM2 downregulation in gingival fibroblasts in IGF.
Keywords: Biglycan; Human gingival fibroblast; Idiopathic gingival fibromatosis; Periodontitis; Specific protein 1; Transglutaminase 2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study protocol was approved by the research ethics committees of Hiroshima University (E2015-0001), and written informed consent was obtained from the subjects. Consent for publication: Consent for publication was obtained from the participants. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

