Maternal infection of SARS-CoV-2 during the first and second trimesters leads to newborn telomere shortening
- PMID: 39574146
- PMCID: PMC11580642
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05879-0
Maternal infection of SARS-CoV-2 during the first and second trimesters leads to newborn telomere shortening
Abstract
Background: Initial telomere length (TL) in newborns is the major determinant for TL in later life while TL in newborn/early-life predicts long-term health and lifespan. It is important to identify key factors that affect telomere homeostasis throughout embryonic development for precision interventions to maintain optimal TL in fetus/prenatal infants. SARS-CoV-2 has caused a widespread global pandemic of COVID-19, but it remains unclear whether maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection impairs prenatal telomere homeostasis.
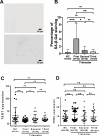
Methods: We recruited 413 normally delivered newborns whose mothers were either non-infected or infected with SARS-CoV-2 during different trimesters of pregnancy (otherwise healthy). Telomere length (TL) in cord blood (CB) was assessed using qPCR. CB and maternal blood were analyzed for cytokine levels. Placental senescence was determined using senescence-associated β-galactosidase staining.
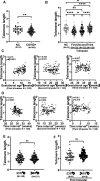
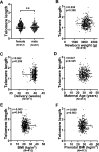
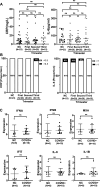
Results: Control (non-infected maternal) newborn TL was significantly longer than that from maternal infection (1.568 ± 0.340 vs 1.390 ± 0.350, P = 0.005). Such shorter TL was observed only if maternal infection of SARS-CoV-2 occurred in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy (1.261 ± 0.340 and 1.346 ± 0.353, P < 0.0001 and 0.001, respectively). There were no differences in TL between controls and infection at the third trimester (1.568 ± 0.340 vs 1.565 ± 0.329, P > 0.05). Across the first trimester, there was a positive correlation between newborn TL and gestational weeks with maternal infection, suggesting that the earlier maternal infection occurs, the worse effect is taken on fetal telomere homeostasis. Placental senescence coupled with the downregulated expression of telomerase reverse transcriptase was significantly more frequent from the maternal infection at the first trimester. There were no differences in IL-6, C reactive protein and other cytokine levels in CB and maternal serum or placentas.
Conclusions: Maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection at the first and second trimesters leads to significantly shorter TL and earlier infection causes much more severe TL damage. The infection-mediated cell senescence and other histopathological abnormalities result in defective placental function through which fetal telomere homeostasis is impaired. Thus, vaccination against COVID-19 should be done in advance for women who plan pregnancy.
Keywords: Maternal infection; Newborns; Placental senescence; SARS-CoV-2; Telomere length.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by Shandong Provincial Hospital Ethics Committees. The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: All authors agree to publish the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Situ Analyses of Placental Inflammatory Response to SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Cases of Mother-Fetus Vertical Transmission.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 13;25(16):8825. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168825. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201511 Free PMC article.
-
Association between maternal urinary manganese concentrations and newborn telomere length: Results from a birth cohort study.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Apr 15;213:112037. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112037. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 33609998
-
Increased DNA damage/repair response in placentas from women infected with COVID-19 in pregnancy.Placenta. 2025 Jun 26;167:152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2025.05.009. Epub 2025 May 14. Placenta. 2025. PMID: 40393216
-
Congenital, Intrapartum and Postnatal Maternal-Fetal-Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 Infections: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 20;12(11):3570. doi: 10.3390/nu12113570. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33233867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 in pregnancy: What we know from the first year of the pandemic.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 Dec 1;1867(12):166248. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166248. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021. PMID: 34461257 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saretzki G. Telomeres, telomerase and ageing. Subcell Biochem. 2018;90:221–308. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

