Bone metabolism in complex regional pain syndrome
- PMID: 39574486
- PMCID: PMC11581760
- DOI: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000001217
Bone metabolism in complex regional pain syndrome
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) often show disturbed bone metabolism, assessed using three-phase bone scintigraphy (TPBS). However, current methods lack automation and standardisation. Bone serum markers have been proposed as biomarkers, but their utility is unclear.
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate bone metabolism in CRPS using TPBS and bone serum markers.
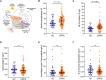
Methods: A deep learning model for automated segmentation quantified tracer enhancement in TPBS images. Serum markers analysed included alkaline phosphatase (AP), 25-OH vitamin D, osteoprotegerin, procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide (PINP), and β-C-terminal telopeptide, compared to 48 healthy controls (HC). The study included 114 patients with CRPS, 41 of whom underwent TPBS.
Results: Of the 41 patients with CRPS with TPBS, 39 (95.1%) displayed radiotracer enhancement in the bone phase across CRPS subtypes. Serum markers of 114 patients did not significantly differ between patients and HC, nor did they correlate with TPBS enhancement, except in warm CRPS. In these patients, TPBS accumulation in the metacarpophalangeal region correlated with PINP (Spearman ρ = 0.63, P = 0.038), and AP levels were elevated at 78 U/L (interquartile range 64-88) compared to cold CRPS at 66 U/L (51-77; P = 0.003) and HC at 60 U/L (53-69; P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Automated TPBS quantification revealed widespread bone metabolism alterations, common in CRPS and detectable beyond qualitative assessment. Although most serum markers remained unchanged, patients with warm CRPS exhibited unique features, suggesting distinct pathophysiological profiles. Integrating novel image analysis with other biomarkers may enhance diagnostic precision and patient stratification for targeted therapies.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Bone markers; Complex regional pain syndrome; Three-phase bone scintigraphy.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The International Association for the Study of Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The University Hospital Wurzburg and HR received patient fees from Gruenenthal and Algiax for the clinical trials. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Aitken SJ, Landao-Bassonga E, Ralston SH, Idris AI. Beta2-adrenoreceptor ligands regulate osteoclast differentiation in vitro by direct and indirect mechanisms. Arch Biochem Biophys 2009;482:96–103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
