Potential Biomarkers for Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 39574502
- PMCID: PMC11578361
- DOI: 10.12865/CHSJ.50.03.01
Potential Biomarkers for Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
Objectives: The study has as main objective the evaluation of the potential roles of vitamin D, the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and the systemic inflammation index (SII) as future biomarkers regarding the classification of flares in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Material and methods: Individuals diagnosed with SLE were encompassed in this observational study. The current applicable criteria, namely The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR)/American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 2019 criteria had to be fulfilled. The participants underwent specific musculoskeletal examination, paraclinical investigations including complete blood count (CBC), determination of serum creatinine levels, as well as liver enzymes, and also the markers of inflammation. The fractions of the serum complement (C3 and C4) were also evaluated, together with serum vitamin D concentrations. Safety of Estrogens in Lupus National Assessment-Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SELENA-SLEDAI) was required in order to analyze the research group's disease activity.
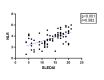
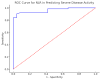
Results: NLR and SII demonstrated validity, having statistically significant correlations with SELENA-SLEDAI (p value less than 0.001). The ROC analysis proved a strong discriminative power for NLR (AUC=0.96) and SII (AUC=0.963) in predicting severe disease flares. Optimal cut-off values were 3.45 for NLR and 877,002.19 for SII. Serum vitamin D concentrations had a weak association with the SLEDAI score (p=0.048, r=0.213).
Conclusions: NLR and SII can be considered reliable biomarkers for discriminating between the levels of disease activity in SLE individuals. Low serum levels of vitamin D may also influence disease severity, but require further validation.
Keywords: NLR; SII; disease activity score; vitamin D.
Copyright © 2022, Medical University Publishing House Craiova.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Kiriakidou M, Ching CL. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81–96. - PubMed
-
- Rivas-Larrauri F, Yamazaki-Nakashimada MA. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Is it one disease. Reumatol Clin. 2016;12(5):274–281. - PubMed
-
- Fortuna G, Brennan MT. Systemic lupus erythematosus: epidemiology, pathophysiology, manifestations, and management. Dent Clin North Am. 2013;57(4):631–655. - PubMed
-
- Zucchi D, Silvagni E, Elefante E, Signorini V, Cardelli C, Trentin F. Systemic lupus erythematosus: one year in review 2023. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2023;41(5):997–1008. - PubMed
-
- Zucchi D, Elefante E, Schilirò D, Signorini V, Trentin F, Bortoluzzi A, Tani C. One year in review 2022: systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40(1):4–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
