This is a preprint.
ComFB, a new widespread family of c-di-NMP receptor proteins
- PMID: 39574629
- PMCID: PMC11581024
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.11.10.622515
ComFB, a new widespread family of c-di-NMP receptor proteins
Update in
-
ComFB, a widespread family of c-di-NMP receptor proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Sep 23;122(38):e2513041122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2513041122. Epub 2025 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40966295 Free PMC article.
Abstract
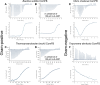
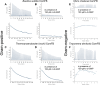
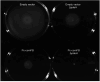
Cyclic dimeric GMP (c-di-GMP) is a widespread bacterial second messenger that controls a variety of cellular functions, including protein and polysaccharide secretion, motility, cell division, cell development, and biofilm formation, and contributes to the virulence of some important bacterial pathogens. While the genes for diguanylate cyclases and c-di-GMP hydrolases (active or mutated) can be easily identified in microbial genomes, the list of c-di-GMP receptor domains is quite limited, and only two of them, PliZ and MshEN, are found across multiple bacterial phyla. Recently, a new c-di-GMP receptor protein, named CdgR or ComFB, has been identified in cyanobacteria and shown to regulate their cell size and, more recently, natural competence. Sequence and structural analysis indicated that CdgR is part of a widespread ComFB protein family, named after the "late competence development protein ComFB" from Bacillus subtilis. This prompted the suggestion that ComFB and ComFB-like proteins could also be c-di-GMP receptors. Indeed, we revealed that ComFB proteins from Gram-positive B. subtilis and Thermoanaerobacter brockii were able to bind c-di-GMP with high-affinity. The ability to bind c-di-GMP was also demonstrated for the ComFB proteins from clinically relevant Gram-negative bacteria Vibrio cholerae and Treponema denticola. These observations indicate that the ComFB family serves as yet another widespread family of bacterial c-di-GMP receptors. Incidentally, some ComFB proteins were also capable of c-di-AMP binding, identifying them as a unique family of c-di-NMP receptor proteins. The overexpression of comFB in B. subtilis, combined with an elevated concentration of c-di-GMP, suppressed motility, attesting to the biological relevance of ComFB as a c-di-GMP binding protein.
Figures




References
-
- Amikam D., and Galperin M.Y. (2006) PilZ domain is part of the bacterial c-di-GMP binding protein. Bioinformatics 22: 3–6. - PubMed
-
- Angerer V., Schwenk P., Wallner T., Kaever V., Hiltbrunner A., and Wilde A. (2017) The protein Slr1143 is an active diguanylate cyclase in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and interacts with the photoreceptor Cph2. Microbiology (Reading) 163: 920–930. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
