This is a preprint.
Hydrophobins from Aspergillus mediate fungal interactions with microplastics
- PMID: 39574658
- PMCID: PMC11580879
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.11.05.622132
Hydrophobins from Aspergillus mediate fungal interactions with microplastics
Update in
-
Hydrophobins from Aspergillus Mediate Fungal Interactions with Microplastics.Environ Sci Technol. 2025 Jul 22;59(28):14528-14539. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5c01771. Epub 2025 Jul 9. Environ Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40631556
Abstract
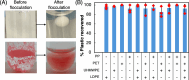
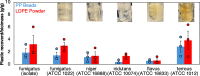
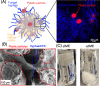
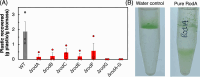
Microplastics present myriad ecological and human health risks including serving as a vector for pathogens in human and animal food chains. However, the specific mechanisms by which pathogenic fungi colonize these microplastics have yet to be explored. In this work, we examine the opportunistic fungal pathogen, Aspergillus fumigatus, and other common soil and marine Aspergilli, which we found bind microplastics tightly. Up to 3.85+/- 1.48 g microplastic plastic/g fungi were bound and flocculated for polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) powders and particles ranging in size from 0.05 - 5 mm. Gene knockouts revealed hydrophobins as a key biomolecule driving microplastic-fungi binding. Moreover, purified hydrophobins were still able to flocculate microplastics independent of the fungus. Our work elucidates a role for hydrophobins in fungal colonization of microplastics and highlights a potential target for mitigating the harm of microplastics through engineered fungal-microplastic interactions.
Keywords: flocculation; fungi; hydrophobin; microplastic.
Conflict of interest statement
Statement of Competing Interests: Work from this manuscript is claimed under pending provisional patent 63/564,151
Figures

References
-
- Ma H., et al. , Microplastics in aquatic environments: Toxicity to trigger ecological consequences. Environmental Pollution 261, 114089 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Khalid N., et al. , Linking effects of microplastics to ecological impacts in marine environments. Chemosphere 264, 128541 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Li H., et al. , Expanding plastics recycling technologies: chemical aspects, technology status and challenges. Green Chemistry 24, 8899–9002 (2022).
-
- Andrady A. L., Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 62, 1596–1605 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Van Cauwenberghe L., Devriese L., Galgani F., Robbens J., Janssen C. R., Microplastics in sediments: A review of techniques, occurrence and effects. Marine Environmental Research 111, 5–17 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
