This is a preprint.
International prevalence patterns of low eGFR in adults aged 18-60 without traditional risk factors from population-based cross-sectional studies: a disadvantaged populations eGFR epidemiology (DEGREE) study
- PMID: 39574842
- PMCID: PMC11581094
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.24.24309380
International prevalence patterns of low eGFR in adults aged 18-60 without traditional risk factors from population-based cross-sectional studies: a disadvantaged populations eGFR epidemiology (DEGREE) study
Update in
-
International prevalence patterns of low eGFR in adults aged 18-60 without traditional risk factors from a population-based cross-sectional disadvantaged populations eGFR epidemiology (DEGREE) study.Kidney Int. 2025 Mar;107(3):541-557. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2024.11.028. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Kidney Int. 2025. PMID: 39708999
Abstract
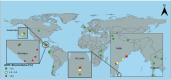
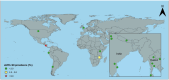
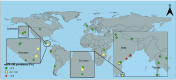
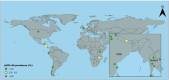
The disadvantaged populations eGFR (estimated glomerular filtration rate) epidemiology (DEGREE) study was designed to gain insight into the burden of chronic kidney disease (CKD) of undetermined cause (CKDu) using standard protocols to estimate the general-population prevalence of low eGFR internationally. We estimated the age-standardised prevalence of eGFR<60ml/min/1.73m2 in adults aged 18-60, excluding participants with commonly known causes of CKD, i.e., ACR>300mg/g or equivalent, or self-reported or measured hypertension or diabetes (eGFR<60[absent HT,DM,high ACR]), and stratified by sex and location. We included population-representative surveys conducted around the world that were either designed to estimate CKDu burden or were re-analyses of large surveys. There were 60 964 participants from 43 areas across 14 countries, with data collected during 2007-2023. The highest prevalence was seen in rural men in Uddanam, India (14%) and Northwest Nicaragua (14%). Prevalence above 5% was generally only observed in rural men, with exceptions for rural women in Ecuador (6%) and parts of Uddanam (6-8%), and for urban men in Leon, Nicaragua (7%). Outside of Central America and South Asia, prevalence was below 2%. These observations represent the first attempts to estimate the prevalence of eGFR<60[absent HT,DM,high ACR] around the world, as an estimate of CKDu burden, and provide a starting point for global monitoring. It is not yet clear what drives the differences, but available evidence to date supports a high general-population burden of CKDu in multiple areas within Central America and South Asia, although the possibility that unidentified clusters of disease may exist elsewhere cannot be excluded.
Keywords: CINA; CKDnt; CKDu; MeN; eGFR; prevalence.
Figures

References
-
- O’Callaghan-Gordo C, Shivashankar R, Anand S, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in India: secondary data analysis of three population-based cross-sectional studies. BMJ Open. 2019. Mar 7;9(3):e023353. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023353. Erratum in: BMJ Open. 2019 Mar 18;9(3):e023353corr1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
