Causal association between plasma metabolites and diverse autoimmune diseases: a two-sample bidirectional mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 39575250
- PMCID: PMC11578997
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437688
Causal association between plasma metabolites and diverse autoimmune diseases: a two-sample bidirectional mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: Autoimmune diseases (ADs) are a category of conditions characterized by misrecognition of autologous tissues and organs by the immune system, leading to severe impairment of patients' health and quality of life. Increasing evidence suggests a connection between fluctuations in plasma metabolites and ADs. However, the existence of a causal relationship behind these associations remains uncertain.
Methods: Applying the two-sample mendelian randomization (MR) method, the reciprocal causality between plasma metabolites and ADs was analyzed. We took the intersection of two metabolite genome-wide association study (GWAS) datasets for GWAS-meta and obtained 1,009 metabolites' GWAS data using METAL software. We accessed GWAS summary statistics for 5 common ADs, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), multiple sclerosis (MS), type 1 diabetes (T1D), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from published GWAS data. MR analyses were performed in discovery and replication stage simultaneously. Meanwhile, the reverse MR analysis was conducted to investigate the possibility of reverse causal association. Furthermore, a series of sensitivity analyses were conducted to validate the robustness of the results. These statistical analyses were conducted using R software. Finally, the web version of MetaboAnalyst 5.0. was applied to analyze metabolic pathways. Ultimately, we conducted ELISA assays on plasma samples from patients to validate the results.
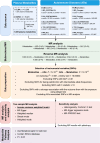
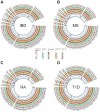
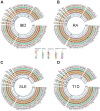
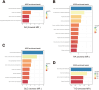
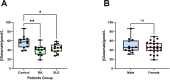
Results: 4 metabolites were identified to have causal relationships with IBD, 2 metabolites with MS, 13 metabolites with RA, and 4 metabolites with T1D. In the reverse MR analysis, we recognized causality between SLE and 22 metabolites, IBD and 4 metabolites, RA and 22 metabolites, and T1D and 37 metabolites. Additionally, 4 significant metabolic pathways were identified in RA by metabolic pathway analysis in the forward MR analysis. Correspondingly, in the reverse, 11 significant metabolic pathways in RA, 8 in SLE, and 4 in T1D were obtained using identical approaches. Furthermore, the protective role of glutamate was confirmed through ELISA assays.
Conclusions: Our research established a reciprocal causality between plasma metabolites and ADs. Furthermore, diverse metabolic pathways correlated with ADs were uncovered. Novel insights into the prediction and diagnosis were provided, as well as new targets for precise treatment of these conditions were discovered.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; autoimmune diseases; inflammatory bowel disease; multiple sclerosis; plasma metabolites; rheumatoid arthritis; systemic lupus erythematosus; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2024 Yuan, Yang, Hu, Cai, Hu, Rui and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

