Efficacy of acupuncture combined with mirror therapy in the treatment of post-stroke limb movement disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
- PMID: 39575345
- PMCID: PMC11580039
- DOI: 10.3389/fresc.2024.1464502
Efficacy of acupuncture combined with mirror therapy in the treatment of post-stroke limb movement disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether the combination of acupuncture and mirror therapy can improve motor impairment in stroke patients.
Design: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.
Data sources: CNKI, Wanfang, PubMed, Embase, Vip, web of since, Cochrane database and CBM database.
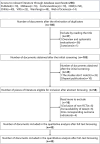
Eligibility criteria for selecting studies: The included randomized controlled trials compared the efficacy of acupuncture therapy (AT) combined with mirror therapy (MT) against AT, MT, and conventional rehabilitation therapy on limb motor impairment in stroke patients, with independent data extraction and study quality assessment conducted. A META analysis using fixed-effect and random-effect models was performed to calculate the mean difference (MD) in motor scores and the Total effective rate RR (Risk ratio) between the AT combined with MT group and the control group.
Main outcome measures: The Fugl-Meyer Assessment (FMA) for motor function includes the FMA-T (total FMA), FMA-UE (upper extremity FMA), and FMA-L (lower extremity FMA).
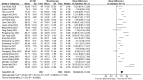
Results: A total of 42 randomized controlled trials were included, involving 3,340 patients with post-stroke motor impairment. AT combined with MT was more favorable for FMA-UE (mean difference [MD] = 6.67, 95% CI [5.60-7.93], Z = 11.42, P < 0.0001), FMA-L [MD = 3.37, 95% CI (2.99-3.76), Z = 17.31, P < 0.001], and FMA-T [MD = 6.84, 95% CI (5.92-7.77), Z = 14.48, P < 0.001]. The combined AT and MT treatment was more favorable for the Modified Barthel Index (MBI) score in post-stroke motor impairment [MD = 10.82, 95% CI (8.52-13.12), Z = 9.22, P < 0.001]. AT combined with MT was more favorable for the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) [MD = -0.34, 95% CI (-0.66 to -0.03), Z = 14.48, P < 0.001]. AT combined with MT was more favorable for the Total effective rate in treating post-stroke motor impairment (relative risk = 1.27, 95% confidence interval [CI] [1.19-1.37], Z = 6.54, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: AT combined with MT can effectively improve patients' motor function and daily living abilities.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO, identifier, CRD42024559992.
Keywords: acupuncture; meta-analysis; mirror therapy; motor impairment; stroke.
© 2024 Ke, Cheng, Ren, Yang, Lai and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
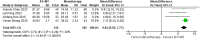















Similar articles
-
Acupuncture combined with mirror therapy for post-stroke dyskinesia: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jun 28;103(26):e38733. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038733. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38941386 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of moxibustion treatment for upper extremity pain disorder and motor impairment in patients with stage I post-stroke shoulder-hand syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurol. 2025 May 23;16:1530069. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1530069. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40488201 Free PMC article.
-
Is acupuncture combined with repeated transcranial magnetic stimulation more effective in improving upper limb motor dysfunction after stroke? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 2;16:1575879. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1575879. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40529441 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of brain-computer interface based training on post-stroke upper-limb rehabilitation: a meta-analysis.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2025 Mar 3;22(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12984-025-01588-x. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40033447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of acupuncture in the treatment of limb dyskinesia after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Nov;27(22):10985-10993. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202311_34467. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38039029
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). The top 10 Ccauses of Ddeath. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed March 10, 2020).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

