APOE ε4-associated heterogeneity of neuroimaging biomarkers across the Alzheimer's disease continuum
- PMID: 39575672
- PMCID: PMC11775459
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14392
APOE ε4-associated heterogeneity of neuroimaging biomarkers across the Alzheimer's disease continuum
Abstract
Introduction: While the role of apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 in Alzheimer's disease (AD) susceptibility has been studied extensively, much less is known about the differences in disease presentation in APOE ε4 carriers versus non-carriers.
Methods: To help elucidate these differences, we performed a broad analysis comparing the regional levels of six different neuroimaging biomarkers in the brains of APOE ε4 carriers versus non-carriers who participated in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI).
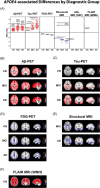
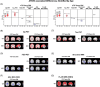
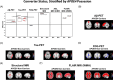
Results: We observed significant APOE ε4-associated heterogeneity in regional amyloid beta deposition, tau accumulation, glucose uptake, brain volume, cerebral blood flow, and white matter hyperintensities within each AD diagnostic group. We also observed important APOE ε4-associated differences in cognitively unimpaired individuals who converted to mild cognitive impairment/AD versus those who did not convert.
Discussion: This observed heterogeneity in neuroimaging biomarkers between APOE ε4 carriers versus non-carriers may have important implications regarding the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of AD in different subpopulations.
Highlights: An extensive study was performed on the apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4-associated heterogeneity in neuroimaging biomarkers from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Robust APOE ε4-associated increases in amyloid beta (Aβ) deposition throughout the brain, in every diagnostic group, were observed. APOE ε4-associated increases in tau pathology, decreases in glucose uptake, and increases in brain atrophy, which expand in regional scope and magnitude with disease progression, were observed. Significant sex- and age-related differences in APOE ε4-associated neuroimaging biomarker heterogeneity, with overall increases in pathological presentation in female APOE ε4 carriers, were observed. Regional differences in Aβ deposition, tau accumulation, glucose uptake, ventricle size, and white matter hyperintensities were observed in cognitively normal participants who converted to mild cognitive impairment/Alzheimer's disease, which may hold potential predictive value.
Keywords: Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; Alzheimer's disease; apolipoprotein E; biomarkers; heterogeneity; neuroimaging.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Tal Nuriel is a consultant for Mubadala Capital. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Blood biomarkers of neurodegeneration associate differently with amyloid deposition, medial temporal atrophy, and cerebrovascular changes in APOE ε4-enriched cognitively unimpaired elderly.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 May 18;16(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01477-w. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38762725 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of APOE ε4 genotype on amyloid-β, glucose metabolism, and gray matter volume in cognitively normal individuals and amnestic mild cognitive impairment.Eur J Neurol. 2023 Mar;30(3):587-596. doi: 10.1111/ene.15656. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Eur J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36448771 Free PMC article.
-
APOE effect on Alzheimer's disease biomarkers in older adults with significant memory concern.Alzheimers Dement. 2015 Dec;11(12):1417-1429. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 May 7. Alzheimers Dement. 2015. PMID: 25960448 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding disease progression and improving Alzheimer's disease clinical trials: Recent highlights from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.Alzheimers Dement. 2019 Jan;15(1):106-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Alzheimers Dement. 2019. PMID: 30321505 Review.
-
Unraveling APOE4's Role in Alzheimer's Disease: Pathologies and Therapeutic Strategies.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2025;26(4):259-281. doi: 10.2174/0113892037326839241014054430. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2025. PMID: 39722484 Review.
References
-
- Alzheimer A, Stelzmann RA, Schnitzlein HN, Murtagh FR. An English translation of Alzheimer's 1907 paper, “Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde”. Clin Anat. 1995;8:429‐431. - PubMed
-
- Reiman EM, Caselli RJ, Yun LS, et al. Preclinical evidence of Alzheimer's disease in persons homozygous for the epsilon 4 allele for apolipoprotein E. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:752‐758. - PubMed
-
- Reiman EM, Caselli RJ, Chen K, Alexander GE, Bandy D, Frost J. Declining brain activity in cognitively normal apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 heterozygotes: a foundation for using positron emission tomography to efficiently test treatments to prevent Alzheimer's disease. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:3334‐3339. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

