Perfusion-Based Relative Cerebral Blood Volume Is Associated With Functional Dependence in Large-Vessel Occlusion Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 39575711
- PMCID: PMC11681566
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.034242
Perfusion-Based Relative Cerebral Blood Volume Is Associated With Functional Dependence in Large-Vessel Occlusion Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
Background: Pretreatment computed tomography perfusion parameter relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) lesion volume has been shown to predict 90-day modified Rankin Scale score in small-core strokes with Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score ≥5, including those with medium-vessel occlusions (mid and distal M2 segment occlusions). Hence, in this study we aim to assess the performance of different rCBV lesion volume thresholds (rCBV <42%, rCBV <38%, and rCBV <34%) with 90-day modified Rankin Scale score including patients with large core (Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score <5) and strictly including only patients with anterior circulation large-vessel occlusion.
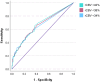
Methods and results: In this retrospective evaluation of our prospectively collected database, inclusion criteria were (1) Computed tomographic angiography confirmed anterior circulation large-vessel occlusion from September 1, 2017, to October 1, 2023; and (2) diagnostic computed tomography perfusion. Student t test, Mann-Whitney U test, and χ2 test were used in the univariate data analysis. Spearman's rank correlation analysis was used to assess correlations. Outcome measure was dichotomized into good functional outcome (90-day modified Rankin Scale score, 0-2) and poor functional outcome (90-day modified Rankin Scale score, 3-6) for logistic regression and receiver operating characteristic analysis. P≤0.05 was considered significant. In total, 229 patients met our inclusion criteria. The majority of the patients (n=161) in our cohort had M1 occlusion. All the rCBV thresholds were significantly higher in patients with poor 90-day functional outcomes and were independently associated with the outcome. Spearman's rank correlation analysis revealed a slightly stronger correlation of rCBV <42% (ρ=0.27, P<0.001), as compared with rCBV <38% (ρ=0.25, P<0.001) and rCBV <34% (ρ=0.24, P<0.001) with functional outcome. Receiver operating characteristic analysis revealed that rCBV <42% (area under the curve, 0.67 [95% CI, 0.60-0.74]; P<0.001) performed marginally better than rCBV <38% (area under the curve, 0.66 [95% CI, 0.59-0.73]; P<0.001), and rCBV <34% (area under the curve, 0.65 [95% CI, 0.58-0.72]; P<0.001).
Conclusions: All the rCBV thresholds were independently associated with poor 90-day functional outcome; however, the rCBV <42% marginally outperformed rCBV <38% and rCBV <34% lesion volumes.
Keywords: poor functional outcome; rCBV <42%; relative cerebral blood volume.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs Lakhani, Albers, Heit, and Yedavalli are consultants for RapidAI (iSchemaView, Menlo Park, CA). The remaining authors have no disclosures to report.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CT perfusion derived relative cerebral blood volume < 42 % is negatively associated with poor functional outcomes at discharge in anterior circulation large vessel occlusion stroke.J Clin Neurosci. 2024 Dec;130:110907. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2024.110907. Epub 2024 Nov 13. J Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39536379
-
The Relative Cerebral Blood Volume (rCBV) < 42% Is Independently Associated with Collateral Status in Anterior Circulation Large Vessel Occlusion.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 10;13(6):1588. doi: 10.3390/jcm13061588. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38541813 Free PMC article.
-
Computed Tomography Perfusion Deficit Volumes Predict Functional Outcome in Patients With Basilar Artery Occlusion.Stroke. 2021 Jun;52(6):2016-2023. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032924. Epub 2021 May 5. Stroke. 2021. PMID: 33947212 Clinical Trial.
-
High relative cerebral blood volume is associated with good long term clinical outcomes in acute ischemic stroke: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Neurol. 2024 Aug 26;24(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03806-w. BMC Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39187761 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral blood volume index in the era of thrombectomy-treated large and medium vessel ischemic strokes.J Neurointerv Surg. 2025 Jan 16:jnis-2024-022609. doi: 10.1136/jnis-2024-022609. Online ahead of print. J Neurointerv Surg. 2025. PMID: 39824593 Review.
Cited by
-
A Combined Approach Using T2*-Weighted Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast MRI Perfusion Parameters and Radiomics to Differentiate Between Radionecrosis and Glioma Progression: A Proof-of-Concept Study.Life (Basel). 2025 Apr 5;15(4):606. doi: 10.3390/life15040606. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283161 Free PMC article.
-
The relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) <42% is independently associated with prolonged hospitalization in anterior circulation large vessel occlusion.Neuroradiol J. 2025 May 31:19714009251348621. doi: 10.1177/19714009251348621. Online ahead of print. Neuroradiol J. 2025. PMID: 40448558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sohn SW, Park HS, Cha JK, Kim DH, Kang MJ, Choi JH, Nah HW, Huh JT. Relative CBV ratio on perfusion‐weighted MRI indicates the probability of early recanalization after IV t‐PA administration for acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016;8:235–239. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011501 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Imaoka Y, Shindo S, Miura M, Terasaki T, Mukasa A, Todaka T. Hypoperfusion intensity ratio and CBV index as predictive parameters to identify underlying intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in endovascular thrombectomy. J Neuroradiol. 2023;50:424–430. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2022.10.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cortijo E, Calleja AI, García‐Bermejo P, Mulero P, Pérez‐Fernández S, Reyes J, Muñoz MF, Martínez‐Galdámez M, Arenillas JF. Relative cerebral blood volume as a marker of durable tissue‐at‐risk viability in hyperacute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2014;45:113–118. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003340 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

