Comparison of the night-time effectiveness in achieving glycemic targets in adults with type 1 diabetes of three advanced hybryd closed-loop systems
- PMID: 39576311
- PMCID: PMC12116888
- DOI: 10.1007/s00592-024-02397-9
Comparison of the night-time effectiveness in achieving glycemic targets in adults with type 1 diabetes of three advanced hybryd closed-loop systems
Abstract
Context: Advanced hybrid closed loop (AHCL) systems currently represent the most advanced modality of insulin therapy.
Aim: To compare the night-time (from 00 to 07 a.m.) effectiveness in achieving recommended glycemic targets of three different AHCL systems in adults with type 1 diabetes (T1D).
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated 55 adults with T1D (mean age 41 ± 16 years, male 40%, diabetes duration 19.4 ± 11.4 years, BMI 24.1 ± 4.1 kg/m2) with similar glycemic control (GMI 7.0-7.4%). Twenty-two participants were using the Minimed 780G system, 18 the Tandem t:slim X2 with Control-IQ system and 15 the DBLG1 system. Continuous glucose monitoring derived metrics and insulin requirement of 14 consecutive nights were analyzed.
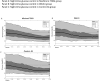
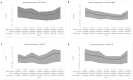
Results: All three groups achieved the recommended mean TIR > 70%, mean TBR < 4%, and mean CV < 36% with a similar insulin requirement (Minimed 780G system: TIR 73.9 ± 11.2%, TBR 0.9 ± 1.2%, CV 29 ± 6.7%; Tandem t:slim X2 with Control-IQ system: TIR 74.1 ± 11.1%, TBR 1.1 ± 1.0%, CV 34.5 ± 6.6%; DBLG1 System TIR 71.7 ± 11.3%, TBR 1.4 ± 3.7%, CV 32.4 ± 7.1%). Tight TIR% (70-140 mg/dl) was significantly higher (p < 0.01) in the Tandem t:slim X2 with Control-IQ group (51.5 ± 9.8%) when compared to Minimed 780G group (42.1 ± 13.7%) and DBLG1 System (40.1 ± 10.5%). In all three groups the insulin infusion similarly decreased from midnight to 05.00 am and then increased.
Conclusions: All the three AHCL systems achieved the recommended TIR, TBR and CV without difference in insulin requirement. The Tandem Control-IQ system obtained a higher tight TIR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: No competing financial interests exist. Informed consent: Written informed consent to use the clinical and biochemical data was obtained from all participants. Ethical standard statement: All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the Ethical Standard of the Institutional and National Research Committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standard. The study was approved by the Local Ethical Committee.
Figures
References
-
- Choudhary P, Kolassa R, Keuthage W et al (2022) Advanced hybrid closed loop therapy versus conventional treatment in adults with type 1 diabetes (ADAPT): a randomised controlled study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 10(10):720–731. 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00212-1 - PubMed
-
- Benhamou PY, Adenis A, Lebbad H et al (2023) One-year realworld performance of the DBLG1 closed-loop system: datafrom 3706 adult users with type 1 diabetes in Germany. Diabetes Obes Metab 25(6):1607–1613. 10.1111/dom.15008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

