One-Year Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of PreserFlo MicroShunt with Mitomycin C Applied by Sub-Tenon Injection Versus Sponge
- PMID: 39576486
- PMCID: PMC11724825
- DOI: 10.1007/s40123-024-01074-y
One-Year Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of PreserFlo MicroShunt with Mitomycin C Applied by Sub-Tenon Injection Versus Sponge
Abstract
Introduction: This study was performed to compare the efficacy and safety of PreserFlo MicroShunt (PMS) implantation with mitomycin C (MMC) applied by sub-tenon injection versus conventional application by MMC-soaked sponges.
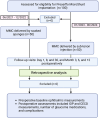
Methods: This retrospective, 1-year cohort study included 100 eyes of 100 patients with glaucoma who underwent PMS implantation with MMC (0.4 mg/ml) delivered either by sub-tenon injection (50 eyes) or via soaked sponges (50 eyes). The primary outcome measure at 1 year was intraocular pressure (IOP) reduction, with complete success defined as an IOP reduction of ≥ 20% and achieving a target IOP of ≤ 21 or 18 mmHg without the use of medication. Secondary outcomes, including corneal endothelial cell density (CECD) loss, the number of medications, and complications, were assessed and compared between the groups.
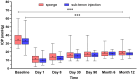
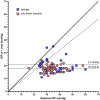
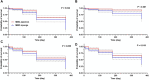
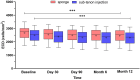
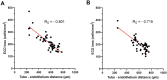
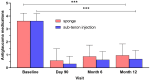
Results: Sustained reductions in mean IOP were observed in both groups over the 1-year follow-up, with no significant differences between the groups. The complete success rate, with a target IOP of ≤ 21 mmHg after 1 year, was 19.3% in the sponge group and 26.4% in the injection group. The qualified success rate was 59.0% and 87.4% in the sponge and injection groups, respectively. A longer survival rate was observed in the injection group than in the sponge group when IOP was below 21 mmHg. The mean CECD significantly decreased (P < 0.01) from baseline to each postoperative follow-up time point in both groups. At 1 year postoperatively, the percentage of total CECD loss was 8.1% in the sponge group and 8.0% in the injection group. However, no significant differences in mean CECD values, the number of medications, or adverse events were found between the groups.
Conclusions: PMS implantation with sub-tenon injection of MMC was comparable in terms of efficacy and safety to traditional MMC delivery via soaked sponges. However, the injection group demonstrated a significantly higher success rate than the sponge group.
Keywords: Corneal endothelial cells; Glaucoma; Glaucoma surgery; Intraocular pressure; MIBS.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: Nora Majtanova and Petr Kolar have the following financial disclosures: Alcon (honorarium); Santen (consultancy and honorarium) and Bayer (honorarium). Adriana Takacova has the following financial disclosures: Alcon (honorarium) and Santen (honorarium). Veronika Kurilova, Libor Hejsek, and Juraj Majtan have no competing interests. Ethical Approval: The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of St. Cyril and Method University Hospital No. 1/9/20/24. Informed consent for surgical procedure was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

