LINC02154 promotes cell cycle and mitochondrial function in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 39576738
- PMCID: PMC11786299
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.16379
LINC02154 promotes cell cycle and mitochondrial function in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
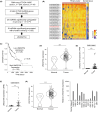
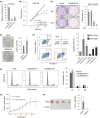
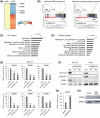
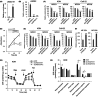
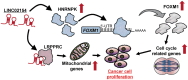
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play pivotal roles in the development of human malignancies, though their involvement in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remains incompletely understood. Using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset, we analyzed expression of 7840 lncRNAs in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and found that upregulation of LINC02154 is associated with a poorer prognosis. LINC02154 knockdown in OSCC cell lines induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and significantly attenuated tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Notably, depletion of LINC02154 downregulated FOXM1, a master regulator of cell cycle-related genes. RNA pulldown and mass spectrometry analyses identified a series of proteins that could potentially interact with LINC02154, including HNRNPK and LRPPRC. HNRNPK stabilizes FOXM1 expression by interacting with the 3'-UTR of FOXM1 mRNA, which suggests LINC02154 and HNRNPK promote cell cycling by regulating FOXM1 expression. Additionally, LINC02154 positively regulates HNRNPK expression by inhibiting microRNAs targeting HNRPNK. Moreover, LINC02154 affects mitochondrial function by interacting with LRPPRC. Depletion of LINC02154 suppressed expression of mitochondrial genes, including MTCO1 and MTCO2, and inhibited mitochondrial respiratory function in OSCC cells. These results suggest that LINC02154 exerts its oncogenic effects by modulating the cell cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in OSCC, highlighting LINC02154 as a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: RNA binding protein; cell cycle regulation; lncRNA; mitochondrial function; oral cancer.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Hiromu Suzuki is an editorial board member of
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long Noncoding RNA LINC00941 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Interacting with hnRNPK in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Nutr Cancer. 2022;74(8):2983-2995. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2022.2027473. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Nutr Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35037538
-
Long non-coding RNA SLC16A1-AS1: its multiple tumorigenesis features and regulatory role in cell cycle in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Cycle. 2020 Jul;19(13):1641-1653. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1762048. Epub 2020 May 25. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 32450050 Free PMC article.
-
LncOCMRL1 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis via the RRM2/EMT pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 30;43(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03190-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39343925 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights on oral squamous cell carcinoma management using long non-coding RNAs.Oncol Res. 2024 Sep 18;32(10):1589-1612. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.052120. eCollection 2024. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39308526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the nexus: Long non-coding RNAs and the PI3K/Akt pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Oct;262:155540. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155540. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39142241 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of LINC00880 promotes colorectal cancer growth.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 May 30;14(5):2926-2939. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-54. Epub 2025 May 23. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40530165 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of LINC02154 promotes esophageal cancer progression by enhancing cell cycling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Noncoding RNA Res. 2025 Jun 2;14:107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2025.06.001. eCollection 2025 Oct. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025. PMID: 40529228 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological Role of LRPPRC in Human Cancers.Cancer Control. 2025 Jan-Dec;32:10732748251353077. doi: 10.1177/10732748251353077. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Cancer Control. 2025. PMID: 40587247 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209‐249. - PubMed
-
- Machiels JP, Rene Leemans C, Golusinski W, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, larynx, oropharynx and hypopharynx: EHNS‐ESMO‐ESTRO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow‐up. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1462‐1475. - PubMed
-
- Vermorken JB, Herbst RS, Leon X, Amellal N, Baselga J. Overview of the efficacy of cetuximab in recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in patients who previously failed platinum‐based therapies. Cancer. 2008;112:2710‐2719. - PubMed
-
- Kiyota N, Hasegawa Y, Takahashi S, et al. A randomized, open‐label, phase III clinical trial of nivolumab vs. therapy of investigator's choice in recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a subanalysis of Asian patients versus the global population in checkmate 141. Oral Oncol. 2017;73:138‐146. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

