Influence of learning stress on anxiety levels among high school students in China: the chain-mediated role of physical activity and mobile phone addiction
- PMID: 39578029
- PMCID: PMC11590819
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-078488
Influence of learning stress on anxiety levels among high school students in China: the chain-mediated role of physical activity and mobile phone addiction
Abstract
Objectives: The objectives are to explore the relationship between study stress and anxiety in high school students and the mediating role of physical activity and mobile phone addiction.
Design: A cross-sectional study.
Setting: 129 high schools were randomly selected in 13 cities of Jiangsu province, China.
Participants: High school students aged 16-19 years, age and gender balance. A total of 40 000 questionnaires were distributed, with 32 974 effectively recovered.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Questionnaires were administered offline, covering four parts: General Demographics, Learning Stress Scale, International Physical Activity Questionnaire, Mobile Phone Addiction Scale and Generalized Anxiety Scale-7. Data analysis included path analysis and correlation analysis, along with descriptive statistics, independent sample t-test, correlation analysis and structural equation model.
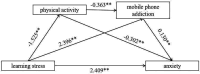
Results: In this study, the proportions of anxiety, high academic pressure, low physical activity level and high mobile phone addiction were 58.18%, 46.48%, 36.40% and 39.26%, respectively. Study stress was positively correlated with anxiety (r=0.130, p<0.01) and mobile phone addiction (r=0.049, p<0.01). Physical activity was negatively correlated with learning stress (r=-0.352, p<0.01), anxiety (r=-0.105, p<0.01) and mobile phone addiction (r=-0.040, p<0.01). The findings were tested by mediating effect analysis that the indirect effect size value of the path 'learning stress → physical activity level → anxiety path' was 0.461, 95% CI of Bootstrap (0.367, 0.554), the mediating effect was significant. The indirect effect size value of the path 'learning stress → mobile phone addiction → anxiety' was 0.072, 95% CI of Bootstrap (0.042, 0.102), and the mediating effect was significant. The indirect effect size value of the path 'learning stress → physical activity level → mobile phone addiction → anxiety' was 0.072, and the 95% CI of Bootstrap (0.226, 0.400), and the mediating effect was significant.
Conclusions: High school students' learning stress can significantly positively predict anxiety levels. High school students learning stress indirectly predicts anxiety through the independent mediating effect of physical activity and mobile phone addiction, as well as the chain mediating effect of physical activity and mobile phone addiction.
Keywords: Adolescent; Cell Phone; China; MENTAL HEALTH.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical