Matrix stiffness drives drop like nuclear deformation and lamin A/C tension-dependent YAP nuclear localization
- PMID: 39578439
- PMCID: PMC11584751
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54577-4
Matrix stiffness drives drop like nuclear deformation and lamin A/C tension-dependent YAP nuclear localization
Abstract
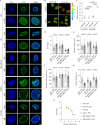
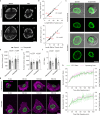
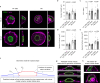
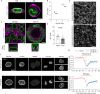
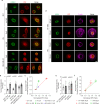
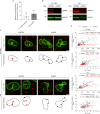
Extracellular matrix (ECM) stiffness influences cancer cell fate by altering gene expression. Previous studies suggest that stiffness-induced nuclear deformation may regulate gene expression through YAP nuclear localization. We investigated the role of the nuclear lamina in this process. We show that the nuclear lamina exhibits mechanical threshold behavior: once unwrinkled, the nuclear lamina is inextensible. A computational model predicts that the unwrinkled lamina is under tension, which is confirmed using a lamin tension sensor. Laminar unwrinkling is caused by nuclear flattening during cell spreading on stiff ECM. Knockdown of lamin A/C eliminates nuclear surface tension and decreases nuclear YAP localization. These findings show that nuclear deformation in cells conforms to the nuclear drop model and reveal a role for lamin A/C tension in controlling YAP localization in cancer cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

