Histone lactylation mediated by Fam172a in POMC neurons regulates energy balance
- PMID: 39578459
- PMCID: PMC11584794
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54488-4
Histone lactylation mediated by Fam172a in POMC neurons regulates energy balance
Abstract
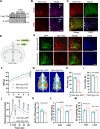
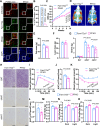
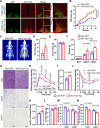
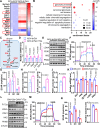
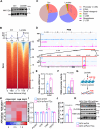
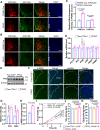
Glycolysis-derived lactate was identified as substrate for histone lactylation, which has been regarded as a significant role in transcriptional regulation in many tissues. However, the role of histone lactylation in the metabolic center, the hypothalamus, is still unknown. Here, we show that hypothalamic pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neuron-specific deletion of family with sequence similarity 172, member A (Fam172a) can increase histone lactylation and protect mice against diet-induced obesity (DIO) and related metabolic disorders. Conversely, overexpression of Fam172a in POMC neurons led to an obesity-like phenotype. Using RNA-seq and CUT&Tag chromatin profiling analyzes, we find that knockdown of Fam172a activates the glycolytic process and increases peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM), which affects the synthesis of α-MSH, via H4K12la (histone lactylation). In addition, pharmacological inhibition of lactate production clearly abrogates the anti-obesity effect of PFKO (POMC-Cre, Fam172aloxP/loxP, POMC neurons Fam172a knockout). These findings highlight the importance of Fam172a and lactate in the development of obesity and our results mainly concern male mice.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Brooks, G. A. The science and translation of lactate shuttle theory. Cell Metab.27, 757–785 (2018). - PubMed
-
- McCarthy, S. F., Islam, H. & Hazell, T. J. The emerging role of lactate as a mediator of exercise-induced appetite suppression. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab.319, E814–E819 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 82325010/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82270894/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82200944/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82470818/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82100908/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

